Excretory Products and their Elimination
Table of Content |

The Excretory System is a biological system that removes unnecessary, excess materials from the body fluids of an organism, to help maintain internal chemical homeostasis and prevent damage to the body. The Excretory System comprises of two kidneys, two ureters, one urinary bladder and a urethra.
What are different nitrogenous products in different organisms?
Ammonotelic
When organisms excrete ammonia as nitrogenous waste, it is known as Ammonotelic. Ammonia is produced by the removal of amino group (-NH2 group) from the amino acids. For Example: Aquatic organisms are usually Ammonotelic.
Ureotelic
When urea is a nitrogenous waste, then the organism is known as Ureotelic. It is an excretory product of humans and other mammals.
Uricotelic
Organisms that excrete uric acid as nitrogenous waste are known as Uricotelic. For Example: Insects, Man etc. In birds, the main excretory product is Uric Acid.
 Excretory System
Excretory System
Ureters
The tube that arises from each kidney is known as ureter. This helps urine to pass from kidney to urinary bladder.
Urinary Bladder
It is a sac-like structure that stores urine before it is discharged from the body. It contains a muscular sphincter that contracts or relax at the time of expulsion of urine from the bladder.
Urethra
The urinary bladder opens into urethra that finally discharge urine from the body.
 Structure of Kidneys
Structure of Kidneys
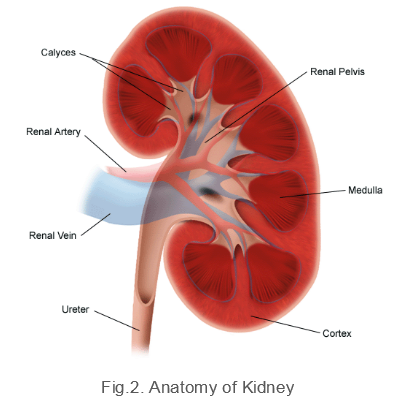
Kidneys are reddish, bean shaped organ that helps in removal of waste from the body. There are 3 layers that surrounds the kidney- Outermost Renal Fascia, Middle Adipose Capsule and Innermost Renal Capsule.
The frontal section of the kidney consists of Outer Cortex and Inner Medulla. The medulla contains cone shaped structures known as Renal Pyramid. The arteries that supply blood to the kidneys are right and left renal arteries.
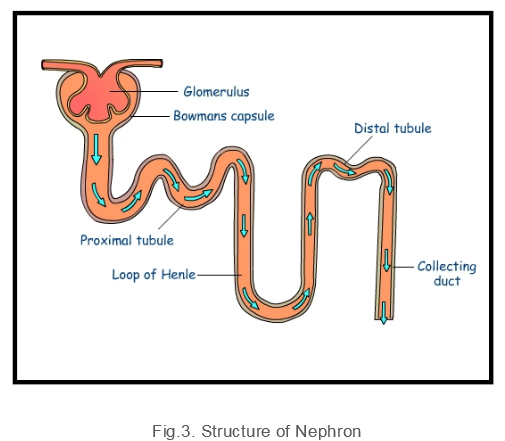
Nephrons
The structural and the functional unit of kidneys is known as Nephron. Each nephron consists of 2 parts - Renal Corpuscles and Renal Tubule. The renal corpuscles comprise of Glomerulus and Bowman’s Capsule. Glomerulus is a tuft of capillaries enclosed in bowman’s capsule. Blood plasma is filtered in glomerular capsule and then the filtered fluid passes into the renal tubule.
The renal tubule comprises of proximal convoluted tubule, loop of distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct.
Urine Formation
3 processes are involved in urine formation:
-
Glomerular Filtration is the first step of urine formation, In this step blood enters the glomerulus via afferent arteriole. This blood is filtered in glomerulus. Water and most solutes are filtered whereas blood proteins and blood cells are not filtered.
-
Tubular Reabsorption is a selective process where water, glucose, amino acids, urea, ions, such as potassium ions, sodium ions, chloride ions etc. are reabsorbed.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule reabsorbs water, sodium ions, potassium ions, glucose, amino acids, urea, bicarbonate ions etc.
Loop of Henle absorbs water, sodium ions, glucose, amino acids, urea, calcium ions, magnesium ions etc. are reabsorbed.
Distal Convoluted Tubule reabsorbs water, sodium ions, chloride ions and calcium ions.
- Tubular Secretion helps in removal of those substances from the body which are not required by the body. For Example: urea, creatinine and some drugs.
Composition of Urine
Urine is a liquid waste product of the kidneys. It comprises of 90% to 96% of water, inorganic salts, some proteins, hormones and variety of metabolites. The yellow color of urine is due to a pigment known as Urochrome.
Watch this Video for more reference
To read more, Buy study materials of Excretory Products and their Elimination comprising study notes, revision notes, video lectures, previous year solved questions etc. Also browse for more study materials on Biology here.