if more than one reaction could occur between a set of reactants under the same conditions giving products that are constitutional isomersand if one product forms in greater amounts than the others, the overall reaction is said to be regioselective.
Say three reactions could occur between the hypothetical reactants A and B under the same conditions giving the constitutionally isomeric products C, D, and E.

There are two possibilities:
1. The three products form in equal amounts, i.e., of the total product 33% is C, another 33% D, the remaining 33% E. (These percentages are called relative yields of the products.)

If this is what is observed, the overall reaction between A and B is not regioselective.
2. One product forms in greater amounts than the others. Say, for example, the relative yields of C, D, and E are 25%, 50%, and 25%, respectively.

If this is what is observed, the overall reaction between A and B is regioselective.
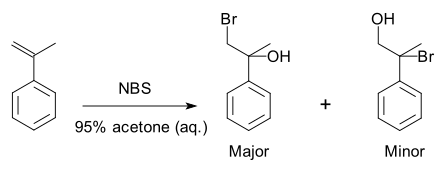
eg:

Experimentally, 2 is the major product; 3 is the minor product. Thus, the overall reaction between 1 and HBr is regioselective toward 2.
If more than one reaction could occur between a set of reactants under the same conditions giving products that are constitutional isomers and if only one product is observed, the overall reaction is said to be 100% regioselective or regiospecific.
eg:

The only observed product is 5. (Relative yields of 5 and 6 are 100% and 0%, respectively.) Thus the overall reaction between 4 and HBr isregiospecific toward 5.
Regiospecificity is merely the limiting case of regioselectivity. All regiospecific reactions are regioselective, but not all regioselectivereactions are regiospecific.
see also chemoselective, stereoselective