Interference by Thin Film
Table of Content |
Colours of Thin Films
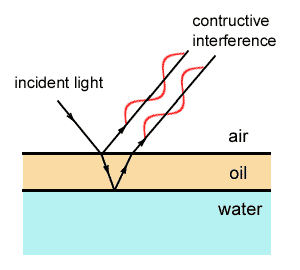
 Everyone is familiar with the brilliant colours exhibited by a thin oil film spread on the surface of water and also by a soap bubble. These colours are due to interference between light waves reflected from the top and the bottom surfaces of thin films. When white light is incident on a thin film, the film appears coloured and the colour depends upon the thickness of the film and also the angle of incidence of the light.
Everyone is familiar with the brilliant colours exhibited by a thin oil film spread on the surface of water and also by a soap bubble. These colours are due to interference between light waves reflected from the top and the bottom surfaces of thin films. When white light is incident on a thin film, the film appears coloured and the colour depends upon the thickness of the film and also the angle of incidence of the light.
Interference in Thin Films
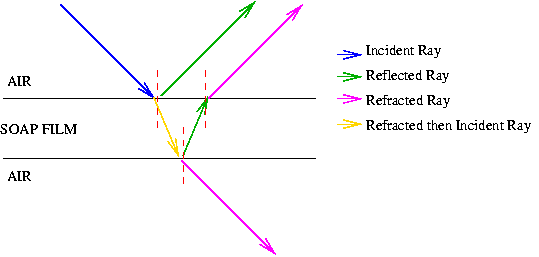
Consider a transparent thin film of uniform thickness t and its refractive index µ bounded by two plane surfaces K and K′ as shown in figure.
A ray of monochromatic light AB incident on the surface K of the film is partly reflected along BC and partly refracted into the film along BD. At the point D on the surface K′, the ray of light is partly reflected along DE and partly transmitted out of the film along DG. The reflected light then emerges into air along EF which is parallel to BC. The ray EH after refraction at H, finally emerges along HJ.
BC and EF are reflected rays parallel to each other and DG and HJ are transmitted rays parallel to each other. Rays BC and EF interfere and similarly the rays DG and HJ interfere.
Interference due to the Reflected Beam
 EM is drawn normal to BC from E. Now the path difference between the waves BC and EF
EM is drawn normal to BC from E. Now the path difference between the waves BC and EF
δ = (BD+DE)in film – (BM)in air
We know, that a distance in air is numerically equal to µ times the distance in medium
δ = µ (BD + DE) – BM
From the figure, it is clear that BD = DE
δ = (2µ . BD) – BM
In the ? BME, sin i = BM/BE [? µ = sin i / sin r]
BM = BE sin i = BE . µ sin r
BM = µ. BE sin r
In the ? BDL, sin r = BL/BD = (1/2 BE)/BD
BE = 2 (BD) sin r
BM = µ(2BD) sin2r
δ = 2µBD – 2µBD sin2r
δ = 2µBD cos2r
In the BDL, cos r = DL/BD = t/BD
So, δ = 2µt cos r
A ray of light travelling in air and getting reflected at the surface of a denser medium, undergoes an automatic phase change of π (or) an additional path difference of λ/2.
Since the reflection at B is at the surface of a denser medium, there is an additional path difference λ/2 .
The effective path difference in this case, δ = 2µt cos r + λ/2
(i) For the constructive interference, path difference δ = nλ, where n = 0,1,2,3 and the film appears bright
2µt cos r + λ/2 = nλ
So, 2µt cos r = (2n-1) λ/2
(ii) For the destructive interference, path difference
δ = (2n+1) λ/2
where n = 0, 1, 2, 3 … and the film appears dark.
2µt cos r + λ/2 = (2n+1)λ/2
2µt cos r = nλ
If light is incident normally i = 0 and hence r = 0. Therefore the condition for bright fringe is 2µt = (2n–1)λ/2 and for dark fringe is 2µt = nλ.
Watch this Video for more reference
Interference due to the Transmitted Light
The path difference between the transmitted rays DG and HJ is, in a similar way, δ = 2µt cos r. In this case there is no additional path difference introduced because both reflections at the point D and E take place backed by rarer medium
Hence, condition for brightness is 2 µt cos r = nλ and condition for darkness is 2µt cos r = (2n – 1) λ/2.
|
|
Problem (JEE Advanced):
One slit of a double slit experiment is covered by a thin glass plate of refractive index 1.4, and the other by a thin glass plate of refractive index 1.4, and the other by a thin glass plate of the refractive index 1.7. The point on the screen where the central maximum fal before the glass plate was inserted, is now occupied by what had been the fifth bright fringe was seen before. Assume the plate have the same thickness t and wavelength of light 480 nm. Then find the value of t in µm.
Solution:
Five fringes have be shifted.
So, 5 = (µ1-1) t – (µ2-1) t / λ
= (µ1 – µ2) t / λ
Thus, t = [5λ / (µ1 – µ2)]
From the above observation, we conclude that, the value of t will be [5λ / (µ1 – µ2)].
Problem:
A soap bubble 250 nm thick is illuminated by white light. The index of refraction of the soap film is 1.36 Which colours are not seen in the reflected light? Which colours appear strong in the reflected light? What
colour does the soap film appear at normal incidence?
Solution:
For destructive interference, we must have nt = mλ/2. Thus, the wavelengths that are not reflected satisfy
λm = 2nt/m,
where m = 1,2,3,.... It follows that,
λ1 = [(2) (1.36) (250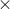 10-9)]/(1) = 680 nm
10-9)]/(1) = 680 nm
and
λ2 = [(2) (1.36) (250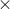 10-9)]/(2) = 340 nm
10-9)]/(2) = 340 nm
These are the only wavelengths close to the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum for which destructive interference occurs. In fact, 680 nm lies right in the middle of the red region of the spectrum, whilst 340 nm lies in the ultraviolet region (and is, therefore, invisible to the human eye). It follows that the only non-reflected colour is red.
For constructive interference, we must have nt = (m+1/2)λ/2. Thus, the wavelengths that are strongly reflected satisfy
λm' = 2nt / (m+1/2)
where m = 0,1,2,.... It follows that,
λ1' = [(2) (1.36) (250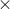 10-9)]/(1/2) = 1360 nm
10-9)]/(1/2) = 1360 nm
and
λ2' = [(2) (1.36) (250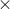 10-9)]/(3/2) = 453 nm
10-9)]/(3/2) = 453 nm
and
λ3' = [(2) (1.36) (250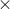 10-9)]/(5/2) = 272 nm
10-9)]/(5/2) = 272 nm
A wavelength of 272 nm lies in the ultraviolet region whereas 1360 nm lies in the infrared. Clearly, both wavelengths correspond to light which is invisible to the human eye. The only strong reflection occurs at 453 nm, which corresponds to the blue-violet region of the spectrum.
The reflected light is weak in the red region of the spectrum and strong in the blue-violet region. The soap film will, therefore, possess a pronounced blue colour.


Question 1
Colours of thin films result from
(a) dispersion of light (b) interference of light
(c) absorption of light (d) scattering of light
Question 2
Two sources of waves are called coherent if
(a) both have the same amplitude of vibrations
(b) both produce waves of same wavelength
(c) both produce waves of same wavelength having constant phase difference
(d) both produce waves having the same velocity.
Question 3
When viewed in white light, soap bubbles show colours, because of
(a) interference (b) scattering
(c) diffraction (d) dispersion
Question 4
Phase difference between any two points situated on a wave-front is:
(a) 2π (b) π
(c) π/2 (d) 0
Question 4
Condition for constructive interference is that the path difference of rays from two sources should be:
(a) even multiple of λ/2 (b) add multiple of λ/2
(c) An integral multiple of λ/2 (d) some other value


| Q.1 | Q.2 | Q.3 | Q.4 | Q.5 |
|
b |
c |
a |
d |
b |
Related Resources
-
You might like to Young’s double slit experiment.
-
For getting an idea of the type of questions asked, refer the Previous Year Question Papers.
-
Click here to refer the most Useful Books of Physics.
-
To get answer to any question related to interference by thin film click here.
You Might Like to Refer:
CBSE online class 10 | CBSE online class 12 |CBSE online coaching
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Click Here Know MoreAsk a Doubt
Get your questions answered by the expert for free