Anatomy of Flowering Plants
Table of Content |
What is Anatomy of flowering Plants?
The study of Internal Structure of an organism is known as Anatomy. Plant Anatomy includes studying of organization and structure of tissues.
Tissue is a group of similar cells that perform specific functions.
Types of Plant Tissue
There are two types of plant tissue: Meristematic Tissue and Permanent Tissue.
Meristematic Tissue
Meristematic Tissue is composed of group of cells that have the capability of division. These cells are responsible for overall growth of the cells.
There are three types of Meristem:
-
Apical Meristem is present on the apices of the root and shoot. It contains actively dividing meristematic cells.
-
Lateral Meristem help plants to grow laterally.
-
Intercalary Meristem is found at the base of nodes and leaf blades. They help the plants to grow and increase in size.
Permanent Tissues
There are two types of Permanent Tissues: Simple and Complex.
- Simple Tissues- There are three types of Simple Tissues. They are as follows:
- Parenchyma is found in Epidermis, Pericycle, Cortex and Pith. They are simple and unspecialized cells. They are involved in Photosynthesis, storage of food etc.
Fig.1. Parenchyma Cells
- Collenchyma are living cells with chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
Fig.2. Collenchyma Cells
- Sclerenchyma Cells are long, lignified cells with tapering ends. These are dead cells and are involved in mechanical function.
Fig.3. Sclerenchyma Cells
- Complex Tissues- It includes Xylem and Phloem.
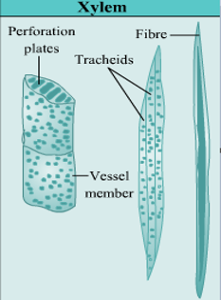
- Xylem is composed of four elements:
-
Tracheid are dead cells with hard, lignified walls. They have tapering, blunt ends. It helps in conduction of water in plants.
-
Vessels are tube-like structures which are dead at maturity. They are involved in transport of water as well as in providing mechanical support to the plant.
- Xylem fibers are lignified with pointed ends. They help in conduction of water and nutrients from root to the leaf.
- Xylem parenchyma are living cells that store starch and fats.
Fig.4. Structure of xylem
- Phloem is composed of following elements:
-
Sieve tubes are slender cells placed end to end. They have perforated ends. They help in conduction of food from the leaves to different parts of the plant.
-
Companion cells are elongated cells. They are present in angiosperms but absent in gymnosperms.
-
Phloem parenchyma are living cells that store food.
-
Phloem fibers provides mechanical strength to the plant.
Fig.5. Structure of Phloem
Watch this Video for more reference
To read more, Buy study materials of Anatomy of Flowering Plants comprising study notes, revision notes, video lectures, previous year solved questions etc. Also browse for more study materials on Biology here.
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More