Class- Amphibia, Raptilia, Aves and Mammalia
Table of Content |
Class- Amphibia
 Devonian origin & carboniferous is the age of amphibians
Devonian origin & carboniferous is the age of amphibians
Class amphibia includes amphibious animals which can live on both the places at ease i.e. under water and on the land. No marine.
These are the first chordate animals which come out of water but these are not able to live on land permanently, these depend on water for their reproduction. Their eggs do not have protecting covering to check the evoporation.
Body is divided into head, trunk and tail. Some amphibians lack tail, e.g. frog, toad etc.
Skin is smooth and mostly scale less, but whenever scales are present there are embeded in the skin e.g. Ichthyophis.
Numerous glands are found in skin which help in moistening the skin. So these animals respire through moist skin. Some poisonous glands are also found in the skin of some animals e.g. Bufo.
Pigment cells are also found as chromatophore for colouration. Few amphibians have ability to change colour by expansion and contraction of pigment cells. This phenomenon is known as Metachrosis.
Two pairs limbs help in swimming in water or moving on land. Forelimbs have four fingers and hindlimbs have five fingers.
Their digits do not have nails or claws at all.
Mouth is bigger in size. Upper or both the jaws have alike teeth. These are pleurodont, homodont and polyphyodont. Suspensorium of jaws is autostylic. (Frog - Acrodont)
A well developed and complete alimentary canal along with digestive glands are present in digestive system (Salivary glands are absent in frog).
Alimentary canal, urinary bladder and genital ducts open into cloaca.
Respiration by gills, skin, lungs or buccopharyngeal cavity.
Two nostrils are found, this condition is called dirhynous.
Heart is three chambered. 2 auricles and 1 ventricle (arteriovenous). Sinus venosus and Truncus arteriosus is well developed.
R.B.Cs are biconvex, oval and- nucleated.
In these animals, renal portal system and hepatic portal system are found.
Endoskeleton is made up of bones, but cranium is cartilaginous.
Skull has two occipital condyles, with the help of these two condyles skull is connected by first vertebra of vertebral column i.e, Atlas, this type of skull is called dicondylic skull.
Ribs absent, but may be present in some animals, but ribs are not attached with sternum.
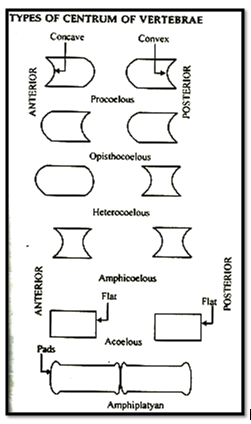
Vertebrae, in these .animals are procoelus type, in which centrum is concave from anterior side and convex from posterior side.
External ear absent, only one ear ossicle columella (stapes) is present in middle ear.
Cranial nerves are 10-pairs.
Lateral line sensory system is necessarily found in any stage of development. In frog it is found only in larval stage.
1 pair of kidneys work as excretory organs. These kidneys are mesonephric' or opisthonephric type. These animals are ureotelic. But tailed animals & larvas are ammoniotelic.
These are cold blooded or poikilothermal animals.
These animals undergo hibernation or aestivation to prevent themselve from extreme cold and heat and to overcome unfavourable conditions.
These are unisexual animals, males have copulatory organs sometimes. These animals return to water from land for their. reproduction.
Fertilization is external and inside the water, but some animals show internal fertilization.
These are oviparous, which lay their eggs in water.
Eggs are mesolecithal. Extra-embryonic membranes are absent, so these are placed under anamniota group.
Cleavage in eggs is holoblastic and unequal.
Development is indirect type i.e. tadpole larva – In Frog: Axolotl larva - In Salamander
This class is divided into three orders:
(A) Gymnophiona or Apoda
(B) Caudata or Urodela
(C) Anura or salientia
(a) Order - Gymnophiona Of' Apoda
Their body is worm like. These are primitive amphibians burrowing in nature.
Their body is limbless.
Skin is soft, and moist, with mucous glands; small scales (cycloid) are found on the skin.
Their eyes are covered by opaque skin. (Blind)
Middle ear and tympanic membrane absent. (Deaf)
Protrusible copulatory organ is present in male.
Fertilization internal.
Parental care is found in them.
Tail ill developed or absent.
e:g. Ichthyophis (Caecilian): Blind worm without tongue.
Uraeotyphlus: Dermal scales are found in the skin.
Gymnophis
(b) Order - Caudata or Urodela
Body is distinctly divided into head trunk and tail.Tail may have caudal fin.
Normally two pairs of limbs are found which are of equal-size. Sometimes hind limb is absent.
Skin is scale less.
Middle ear arid tympanic membrane absent.
External gills are present only in larval stage.
Copulatory organ absent in males.
Fertilization is internal.
Vertebrae are numerous their centrum is amphicoelous or opisthocoelous type.
Characterstic feature of this order is neoteny. Larva attains sexual maturity without undergoing metamorphosis, and starts reproduction.
e.g.:
Salamandra: It is viviparous. Its larva is called Axolotl larva. It sometimes show neoteny. (Longest gestation period - 36 months)
Proteus - Cave - salamander (Blind)
Ambystoma - Tiger salamander (Axolotl larva)
Triton - Newt
Neciurus - Water dog or mud puppy:- Gills in adult also. It shows permanent neoteny.
Amphiuma - Congo-eel - Largest RBC is present Siren - Mud-eel
Cryptobranches - Hell Bender: Largest Amphibian, Fully aquatic.
(c) Order: Anura or salientia:
These are specific animals where tail is absent in adult stage.
All the frogs and toads are included in this order,
Skin is moist with mucous.
2 pairs of limbs are found. Fore 'limbs are short and hind limbs are long.
Gills are absent in aduts.
Vertebral column small, in which only 5 - 9 vertebrae are found. Last vertebra is -stick like urostyle.
Eyes with lids, tear glands present. (Lower lid movable & upper immovable).
Maxillary teeth are present in the upper jaw (absent in toad).
Middle ear and Tympanic membrane present.
Egg laying, fertilisation and development is always in water.
These have well developed vocal sacs i.e. power of voice.
Fertilization external.
Development indirect i.e. tadpole larva is found in them.
Metamorphosis complete:
e.g.:
Bufo - Common toad [Poision glands are modification of parotid gland.
Hyla - Tree - frog
Rana tigrina - Indian bull frog. Mentomechanical bond is found (Tip of the lower jaw).
Rhacophorus - Flying frog
Alytes - Midwife toad - Parental care is well developed in them. Male toads carry eggs in their limbs.
Pipa americana - Surinam toad - carries eggs,
Secondary vivipary. (Tongue absent)
Rana goliath - Largest frog
Phyllobates - Smallest frog (found in Cuba)
Discoglossus or Bombinator - Free bellied toad.
Xenopus - African toad
Review
Amphibia (amphibians): First land vertebrates, evolved from lobe - finned bony fishes; skin naked and moist for respiration, have four limbs, digits without claws, sac-like lungs, 3-chambered heart, undergoes metamorphosis, embryonic membranes not formed.
Reptilia
Reptila were originated during carboniferous period of palaeozoic era. Mesozoic era is Golden age of Reptile.
The branch of biology which deals with the study of reptiles is known as "Herpatology".
Class Reptila’s animals are the first successful terrestrial animals.
First reptiles are called stem reptilia or Cotylosours.
General Characters of Reptilia
These are, normally, terrestrial animals, but some animals are aquatic in nature also.
Body is divided into head, neck, trunk and tail.
Their skin is dry, cornified, rough, nong-landular (Femora; gland in male lizard).
In these animals, each limb has five digits. Each digit has mcurved nails.
Some lizards and snakes do not have limbs e.g.Ophiosaurus lizard is a limbless lizard is a limbless exoskeleton is made up of horny epidermal scales or bony scales or bony plates. A complete alimentary canal is found in these animals, which opens into cloaca.
Teeth are acrodont and thecodont pleurodent type.
Tongue is protrusible.
Respiration in these animals is by lungs, through out the life, but members of order Chelonia can respire through their cloaca, it is known as "Cloacal respiration".
In these animals, heart is incompletely four chambered with 2 complete auricles and two incomplete ventricles. Right and left both systemic arches are present.
Ventricle of animals of order crocodifia is completely divided into two, i.e. heart is four chambered in crocodiles.
Sinus venosus is ill developed and truncus arterious is absent. RBCs are oval and nucleated.
Endoskeleton of these animals is made up of bones.
Only one occipital condyle is present in skull, this type of skull is called monocondyl skull. Ribs are present in neck and thorax ribs of thoracic region make true sternum.
Centrum of vertebrae are procoelus type. Sternum is well developed. Sternal ribs are found in reptiles.
A chevron bone is found in caudal vertebrae of these animals.
One pair of metanephric kidneys help in excretion. These animals are uricotelic for water conservation.
There are 12 - pairs of cranial nerves in these animals.Brain is well developed.
Lateral line system is absent. At the roof/ceiling of buccal cavity Jacobson's organ (olfactory) is present.
Genital aperture is not separate from anus. Ureters, genital ducts and alimentary canal open into a single cloacal aperture.
These are unisexual animals. Fertilization is internal.
One or two penis (Hemipenis) is found in male animals as copulatory organ.
These are mostly oviparous, but some animals are viviparous also. Amount of yolk is very much in their eggs, i.e. eggs are Polylecithal & Telolecithal.
Eggs are cleidoic, i.e. eggs are covered by a shell made up of CaCO3·
Cleidoic eggs is an adaptation for terrestrial habitat. Eggs are leathery.
All the three embryonic membranes amnion, chorion and allantois are present in the embryo. Yolksac is also attached with embryo. So this class is grouped under Amniota group.
Cleavage is discoidal, meroblastic.
Development direct i.e. larva stage is absent.
Parental care is often marked.
hese are cold blooded, poikilothermal animals.
Their body temperature varies according to climate.
Class Reptilia is classified on the basis of presence or absence of temporal fossae in the temporal region of skull and on their number.
Class reptilia is divided into following major five sub-classes
(1) Anapsida
(5) Diapsida
Subclass - Anapsida
Temporal fossae are absent in the temporal region of the skull i.e. roof of skull is complete.
Limbs are strong.
(1) Order - Cotylosauria
e.g. Seymauria: Connecting link between Amphibia and Reptilia.
(2) Order - Chelonia
Body is broad and oval.
They are terrestrial, marine and freshwater animals.
This order includes live and extinct both the animals.
Whole body is covered by firm bony shell.Exoskeleton of dorsal region of body is called carapace and skeleton of ventral region of body is called plastron.
Jaws are horny and teeth less, beak like jaws are found.
Sternum is absent:
Bony plate present on the body are called osteoderms.
Nails are found on digits. Web or membrane is found in the digits for swimming.
Scales are found on neck, limbs and tail.
All these three organs can be pushed into the carapace.
Thoracic vertebrate and ribs are attached with carapace.
Cloacal aperture is vertical and it helps in respiration.
Single copulatory organ is found in male animal.
Animals are oviparous.
e.g.
Testudo - Land tortoise
Trionyx - Fresh water terrapins (edible)
Chelone – Marine’ (tortoises) turtles
Kachhugra tactum
Sub-class - Diapsida
One pair superior and one pair inferior temporal fossae are found in the temporal region of skull.
Subclass Diapsida is divided into two super orders
(1) Lepidosauria
(2) Archosauria
(1) Super order Lepidosauria:
This super oreer-is divided into two orders.
(1) Order - Rynchocephalia
Most of the species of this order are found in the form of fossils.
Only Sphenodon punctatum species is live only. It is found in New Zealand.
Body is small and lizard like. Tail is compressed laterally.
Limbs are pentadactyl and digits are with nails.
A functional third eye or pineal or parietal eye is found in the head.
Vertebrae are amphicoelus type.
Teeth are acrodont type.
Penis or copulatory organ is absent in male animals.
Long living » 100 years
e.g; Sphenodon punctatum - Tuatara (living fossil) It is found only in Newzealand.
(2) Order - Squamata:
Largest number of species of reptiles is found in this order in modern era. All the lizards & snakes are included in this order.
One or two pairs of temporal fossal are found in temporal region of skull, which disappear after sometimes.
Limbs clawed, Limbs are absent in snakes and some of the lizards.
Horny scales are found on body, i.e. their exoskeleton is made up of horny plates.
Vertebrae are procoelus type.
Teeth are pleurodont, i.e. tooth is situated at lateral side of jaw bone.
Copulatory organs are can be seen paired (hemipenis).
Autotomy phenomenon in lizards.
Order squamata is divided into two suborders Suborder
(i) Lacertilia Suborder
(ii) Ophidia
Suborder (i) Lacertilia:
Normally the members of this suborder is "Lizards"
Study of lizards is called "Saurology",
Limbs and girdles are well developed in these animals.
Eyelids are movable and nictitating membrane is found in eye.
Auditory aperture or auditory opening and tympanum is present
Urinary bladder is present
Foramen of panizzae is present in the heart of lizard.
e.g.
Hemidactylus - Common lizard, wall lizard. It can shed its own tail at the time of emergency.
It is called autotomy. Power of regeneration is well marked.
Calotes - Blood sucker, Garden lizard (Girgit). It can change its colour according to environment.
Draco - Flying lizard. Its body skin expands in the form of 2 wings or patagia. With the help of these patagia, it can glide from one tree to another tree or its branches. It can not fly.
Chameleon - Arboreal lizard (Viviparous) (Girgit)
Varanus - Goh, Monitor lizard.
Varanus komodoensis -Ferocious Dragon - Largest living lizard
Ophio-saurus - It is limbless lizard. It is also called glass - snake.
Anguis - limbless lizard
Burkudia - limbless lizard found in south India.
Heloderma - Gila - monstor, Hela monster. It is the only poisonous lizard. Its poison glands are modified sublingual glands (Mexico & USA).
Mabuya - Viviparous lizard.
Phrynosoma - Horned toad (viviparous)
Amblyrhynchus - Marine lizard
Uromastix - Sand lizard or Sand a
Suborder (ii) Ophidia:
Members of this suborder are normally called "Snakes".
The study of snakes is called ophiology or serpantology.
Body long, thin, smooth and limbless,
Eyelids are immovable and nictitating membrane - in eyes are absent.
Girdles, sternum and urinary bladder absent.
Auditory opening and tympanum absent. No middle ear
Tongue thin, long and bifid and sensitive to odour and vibration.
Left lung is ill developed.
Leathery shell is found on egg of Snakes. e.g.
Python molurus - Azgar. It is the largest snake, its length is about 5 feet. Rudiments of hind limbs are found on the body. It is non-poisonous snake.
Ptyas mucosus - Zamenis or Rat snake. It is commonly called Dhaman. It feeds on rats, so it is also called "Friend of farmer". It is non-poisonous snake.
Eryx Johni - Sand boa. It is also called Dumuhi snak. It is a non-poisonous snake.
Typhlops - Blind snake. Non-poisonous
Hydrophis - Marine snake. It is a deadly poisonous snake. Its tail is laterally compressed. It is a viviparous snake.
Enhydrira - Sea snake
Naja - Indian cobra, poisonous snake. Its poison is neurotoxic.
Naja bungarus or N.Hannah - King cobra, poisonous snake. It is the largest snake and poisonous snakes (Head with one or two circular mark).
Bungarus - Krait: Poisonous (neurotoxic) snake Vipera - Viper snake: Head is differentiated from body. Poisonous snake (viviparous). Its venum is haemotoxic/Cardiotoxic. Loreal pit is found which is a thermoreceptor. Largest viper is Russel viper (N mark on head).
Micrurus - Coral snake.
Crotalus - Rattle snake: It produces a characteristic rattling sound of "Rate-raterate", so it is called rattle snake. It is poisonous and ovo-viviparous snake.
Characteristic features of poisonous snakes:
Small scales are found on head or hood.
Laterally compressed tail is present in marine snake.
Ventrally placed scales of the body arc broad.
Two teeth mark is of poisonous snake. (V-shaped - Non poisonous)
Poison glands of poisonous snakes are modified labial glands. These are homologous to salivary glands of Mammals.
Poisonous teeth (fangs) are modified maxillary teeth.
Treatment of poisonous snake bite is done by Antivenom dose.
Anti-venom is produced at
(1) Central Research Institute Kausuali - Shimla
(2) Hoffkine Institute, Mumbai.
Biggest Serpentorium is located in India-Chennai
(2) Super order - Archosaurea
This super order is classified into
(1) Order - Crocodilia or Loricata
(2) Order - Saurischia
Order - Crocodilia or Loricata
Crocodiles, alligator etc. are included in this order.
These are amphibious in nature these live in lakes or rivers.
These are largest modern reptiles.
Skin is covered by lines of bony scutes
Body is solid and massive.
Snout is long. External nares are situated at the distal end of snout and nares have cover also.
Diaphragm is present in between thorax and abdomen.
Sternum and abdominal ribs are present.
Special features:
- Heart is completely four chambered
- Ventricle is completely divided into two chambers.
- Teeth are thecodont type.
Urinary bladder absent
A median erectile grooved penis is present in male animals e.g.
Crocodylus/Crocodilus (Crocodile) - It is only found in
Indian subcontinent.
Gavialius - Gharial. Snout very long.
Alligator - Mexican crocodile.
Order - Saurischia
Order of reptilian pinosaurs (fossils)
Found in Jurassic, Triassic period of Mesozoic era Extinct in Creataceous period of Mesozoic era.
e.g.
Brontosaurus - Thunder lizard. Largest Dinosaurs (Herbivorous).
Tyrannosaurus - Tyrant lizard. King of Dinosaurs
Review
Reptilia (reptiles): Dry scaly waterproof skin, digits of all the four limbs armed with claws, well developed lungs for air breathing, incompletely 4- chambered heart in most cases, males with copulatory organs, eggs amniotic and laid on land, fertilization internal, no larval stage.
Class – Aves
Birds are originated at the end of Jurassic period of Mesozoa era & modernisation in cretaceaous
Study of birds is known as "Ornithology"
Dr. Salim Ali was the great ornithologist of India and known as "Birdman of India"
Study of bird's egg is known as Oology.
Study of bird's Nest is known as Nidology.
Birds are glorified reptiles stated by Huxley.
Arrangement of wings on the body of bird is known as Pterylosis.
Main Characters
All types of birds are included in this class.
Body is boat shaped: It is divided into head, neck, trunk and tail. Neck is long and flexible.
A cover of soft feathers (derivative of stratum corneum) is present all over the body of all the birds, that is called "plumage"
Scales are found only on hind limbs.
Skin is dry and without glands. But oil glands or Preen glands are found on tail or Urophygium. These glands secrete oil, which softens and makes greasy to the feathers.
Two pairs of limbs are present.
Forelimbs (with three digits) are modified into wings, which help in flying and in conserving heat.
Four clawed digits are found on hind limbs.
A three chambered cloaca is present in the birds.
Teeth are absent in jaws. Jaws are modified into horny beak. Beak is toothless. An epidermal horny sheath is present on beak, which is called Ramphotheca.
Spongy lungs are present for respiration. Air sacs are also found, these help in flying.
Sound producing organ at the junction of trachea and bronchi of birds is called syrinx.
Heart is four chambered.Hepatic portal system is well developed in birds, but renal portal system is ill developed. Sinus venosus is absent. Only right aortic arch persist.
R.B.Cs are nucleated.Endoskeleton is bony. These bones are hollow, in which air is filled; these bones are called pneumatic bones. These make the body light in weight and help in flying.
A single occipital condyl is found in skull i.e. birds are monocondylic.Centrum of the vertebra is heterocoelous.
Last four caudal vertebrae fuse to form pygostyle.
Sternum is large. Swollen basal-part of sternum is called "Keel" This keel offers a joint plane for flight muscles.
Keel 18 highly developed in flying birds.
Ribs of birds are bifid and uncinate processes are present in ribs.Exoskeleton is in the form of soft feathers all over the body (except hind limbs). Foramen of triosseus is found in their pectoral girdle.Two bones, clavicle and interclavicle fuse to form 'V-shaped furcula.Furcula is also known as Wish bone or Merry thought bone, which act as a spring between two girdles.Furcula is absent in flight less birds.
Kidneys metanephric (Trilobed). Ureters open into cloaca.Members of class Aves are always uricotelic,
Uric acid is a semisolid substance. Excreta of marine birds is known as guano.Most of the birds do not have urinary bladder and copula toy organ.
Brain is large, smooth, highly developed.Cerebellum is well developed for aerial mode of life.Cranial nerves are 12-pairs.
The skin around the nostrils in birds, is called "Cere".Eyes are large and well developed which are surrounded by rings made 'up of bony plates known as selerotic ossicles.Eyes are large and nictitating membrane is present in eye. Vision is unilocular.
A specific comb like structure pecten is found in the eyes of all birds execept kiwi's eyes. Pecten helps in accomodation of eye and provides nutrition to eye balls. It also controls the pressure of liquid present in eye vision and telescopic vision of birds is due to pecten.
External ears are present but ear pinnae are absent.
Columella bone (Stapes) (one ossicle) is found in middle ear. Cochlea (not coiled) is present in internal ear.
Olfactory organs are less - developed.Birds are monodelphic i.e. only left ovary and left oviduct is functional in females. Birds are oviparous vertebrates.Birds are unisexual. Sexual dimorphism is well marked. Copulatory organ is absent in males.
Fertilization is internal.They are egg laying i.e. oviparous.Eggs are large, megalecithal, telolecithal and cteidoic. Shell is perforated. Cleavage is discoidal meroblastic.Embryonic development is direct. Embryonic membranes are present, so birds are included under group amniota.All the birds form nests. Parental care is well marked. Young one without feather is known as Nidiculous and with feather is known as Nidifugous.
Birds are warm blooded or homeothermic or endothermic animals i.e. Body temperature remains almost constant, what ever may be the temperature of atmosphere around these birds.
Class Aves is divided into 2 subclasses – Subclass
(a) Archaeornithes, Subclass
(b) Neornithes
- Subclass - Archaeornithes
Primitive "Lizard like birds:' are included in this subclass, which belong to Jurassic period. All the members have become extinct.
Wings are ill developed, i.e. capacity of flying was very less.
Pygostyle was absent.
Keel on sternum was absent.
There were present 3 - 3 clawed digits of forelimb at the free edges of wings.
Uncinate processes on ribs were absent.
Teeth were present in the jaws of skull.
All the members of this subclass are the connecting links between reptiles and birds.
E.g.
Archaeopteryx - Lizard bird. (Extinct in Cretaceous period) Its fossil was discovered by Andreas wagner in 1861 from Bavaria (Germany).
Sub class - Neornithes
This subclass includes mostly live animals and extinct animals of post jurassic period.
Wings are well developed which are used in flying (except some birds)
Last few vertebrae fuse to form pygostyle.
Sternum is bigger and with keel.
Digits of forelimbs are fused and claws absent.
Thoracic ribs are having uncinate processes.
Except some species (which are extinct) rest all the birds are toothless.
In live members of this subclass, vertebrae are heterocoelous:
This subclass is classified under four super orders.
(i) Super order - Odontognathac:
These extinct animals were having teeth
Pygostyle was absent.
Keel in sternum is absent e.g. Hesperornis
(ii) Super order - Impennae
All the members of this super order are aquatic birds
Forelimbs are modified into flippers * Limbs are webbed.
Teeth are absent
Sternum without keel.
e.g.Spheniscus - Penguine - It is also called "sea bird of Antarctica".
(iii) Super order - palaeognathae or Ratitae
It includes large and massive birds, which are flightless in nature.These are able to run fast. Wings are reduced, rudimentary, vestigeal or absent.
Caudal vertebrae are free and pygostyle is absent.
Sternum is raft like which lacks keel.
Uncinate processes on ribs are absent.
Oil glands or preen glands absent.
Sound producing organ syrinx is absent. e.g.
Struthio - African ostrich or Camel-bird - It is the largest living bird of modern period. It is almost 8 feet in height. Polygamous, male incubate the eggs (Largest egg). In this bird urinary bladder and penis is present.
Rhea - American ostrich - It also has urinary bladder and penis.
Apteryx - Kiwi - It is National bird of New zealand. It has hair like feathers all, over its body. It is smallest' flightless bird.
Dromaeus- Emu-It is a monogamous bird in which only males look after their young ones and eggs.
Aepyornis - Elephant bird
Casuarius - Cassowary (found in new Guina)/Austrails
(iv) Super order - Neognathae or Carinatae
This super order includes small sized flight birds of modem era. Wings are well developed.Pygostyle is presentKeel in sternum is highly developed - Its crop glands secrete pigeon milk.Uncinate processes at ribs are well marked.Oil glands or preen glands are found.Beak is toothlessSound producing syring is present.
e.g.
Pavo-cristatus - Peacock - It is the national bird of India.
Psittacula krameri - India parrot (uper jaw movable - Psittaciformes)
Columba livia - Blue rock region. Its crop gands secrete pigeon milk (columbiformes)
Streptopelia - Dove
Passer domestieus - Sparrow - It shows commensalism with man.
Corvus splendens – Crow
Molpaster - Bulbul
Cygnus - Swan - Aquatic bird having webbed limbs
Dobo bobo - Bubo or owl or III of omon"
Cuckoo - It lays it eggs in the nest of other birds
(Crow)
Anas - Duck
Phoenicopterus - Flemingo
Alcedo - King fisher
Ardea - Grey heron
Dinopium - Wood peeker - Kathphorva
Albatross - Diomedea - Marine bird with largest wings in flying birds.
Milvus - Kite (Predatory birds)
Falco - Falcon (Predatory birds)
Neophron - Vulture (Scavenger bird)
Choriotis-nigriceps- Great Indian bustard. It is also called Gondavan. It is the state bird of Rajasthan.
Helena - Humming bird - It is also called sunbird. It feeds on nectar of flowers. It is the smallest bird. It is found in Cuba. It can fly in forward and backward both the directions. It can fly like helicoptor. Its size is about 3 to 4 cm.
Ploceous - Weaver bird (Baya)
Micropodus - Pitohiudicthous/pathua - It is the only one poisonous bird, which is found in New guinea.
Swift spine tailed - Fastest flying bird, it is found in Japan.
Poor bill - Bird which shows sleeping stage and undergoes hibernation.
Migratory birds:
Pluvianlis dominica - It is an american bird which migrates from south to north and from north south.
Scolopax eusticola - It migrates from hill area planes.
Himidyan partiges - It can fly over 6000 miles
Sterna parasisaea - Champion bird - Arctic to Antarctic and back.
Bird Sanctuary
Keveladev Ghana bird Sanctuary (largest) Bharatpur (Rajasthan)
Sultanpur (Lake) bird Sanctuary - Gurgao (Haryana)
Govind Sagar bird Sancturary - Bilaspur (Haryana Chilka lake bird Sancturary - Balagaon (Orris a)
Feathers:
There are different types of feather namely (1) Quill (flight feather) consists of (a) Remiges - feather of wings (b) Retrices - feather of tail (2) Coverts – small just like quill for filling gap on wings & tail.
(3) Contours - small feather to cover the body
(4) Filoplums - Beneath the contours (5) Down feather - Cover the body of newly hatched bird.
Review
Aves (birds): Thin dry skin convered with feathers that conserve body heat/ forelimbs modified into wings, fingers without claws, toes aimed with claws, spongy little elastic lungs have air - sacs opening into them, voice box, called syrinx, is at the bifurcation of trachea into bronchi, heart is 4- chambered, eggs amniotic, fertilization internal, no larval stage, endothermic, generate body heat by rapid metabolism, nest building, parental care/ migratory behaviour.
Class Mammalia
Mammals were evolved in Triassic period of Mesozoic era. Coenozoic era is golden era of mammals.
Study of mammals is known as Mammology.
Main Characters:
The members of this class are cosmopolitan.These are highly developed animals.
Body is divided into head, neck, trunk and tail.
A horizontal, diaphragm is present in the body cavity of all the members of this class without any exception.
This diaphragm is present in between thorax arid abdomen.This helps in respiration, defaecation, micturition arid parturition.
Their body is covered by a coat of hair (made of a Keratin), called pelage.
Skin of mammals is thick, water proof, glandular. So many types of glands are present in the skin as sweat glands, oil glands or sebaceous glands and mammary glands.
Mammary glands (Modified sweat glands) are found in females for baby feeding, so on the basis of this/ the class mammalia was so named.
Mostly horns are present at head, nails at digits, claws or hoof are found/ which provide protection.
Two pairs of limbs are present in trunk. Limbs are pentadactyle which help in swimming, walking/ running etc. Hind limbs are absent in Cetacea and Sirenia.
Alimentary canal is complete, its proximal end is called mouth and distal end is called anus. Anus and urinogenital apertures are separate. Cloaca is absent (Exception-members of Prototheria have cloaca)
Teeth are fixed in sockets in the buccal cavity, so teeth are called Thecodont.
Teeth are of four types i.e. such type of teeth are called Heterodont teeth.
Teeth come out two times in a life span in most of the animals so these are also called diphyodont teeth.
Suspensorium of their jaws is craniostylic type.
Lower jaw is made up of dentary bone.
Respiration is by one pair of lungs (Enclosed in pleural cavity).
Larynx or sound organ is found in the neck region for the production of sound.
Heart four chambered. Double circulatory system is present. No sinus venosus. Only left aortic (systemic).
RBCs small, circular and non nucleated except, family camilidae (Lama) and Camel which has nucleated RBCs.
Endoskeleton is bony, skull is dicondylic.
Vertebrae are acoelous or amphiplatyan type i.e. centrum is flat at both the sides. Cartilaginous pads are found at the edges of centrum, that are called epiphysis.
Neck is having 7 cervical vertebrae except:
Bradypus/sloth has 9 or 10 cervical vertebrae and Sea - cow / mantees has 6 cervical vertebrae.
Ribs are bifid.
One pair of Metanephric kidneys are situated in abdominal cavity. These animals ate ureotelic.
Brain is comparatively large and highly developed.
Cerebrum and Cerebellum are very complex in structure and highly developed.
A special structure is present for the connection of both the cerebral hemispheres of brain, that is called corpus - callosum. (Absent in Monotermes & Marsupial)
Optic lobes are four in number and are solid. All the 4 optic lobes collectively known as corpora quadrigemina.
Cranial nerves are 12-pairs
External ear is present in the form of ear pinna.
Malleus, Incus and stapes are the three ear ossicles in middle. ear.
Cochlea of internal ear is highly coiled spirally.
Mammals are unisexual animals. Testes of males are situated (outside the body) in the scrotal sacs. A distinct penis is present in males for copulation,
Ovaries and a reduced penis clitoris is found in females.
Fertilization is internal and it takes place in fallopian tubes.
Eggs are developed in uterus. Embryonic membranes amnion, chorion and allantois and yolk sac are found in embryo so these are grouped under group Amniota.
Eggs are alecithal or microlecithal & homolecithel but eggs of prototherians are megalecithal.
Embryo is attached through the uterus of mother by placenta, so these animals are also called placental animals.
Placenta helps in the nutrition, respiration and excretion of embryo.
Mostly mammals are viviparous, which give birth to their young ones. Some mammals are oviparous [Prototherians], some mammals are ovoviviparous. [Metatherians].
Parental care is well marked in mammals. Mother feeds the child by milk secreted by her mammary glands and looks after her child.
Mammals are warm blooded and. homeothermic or endothermic animals
Livings mammals are classified into two subclasses
Subclass: Prototheria
In this subclass primitive egg laying mammals are included.
Eggs are large, yolky and shelled. (Megalecithal)
Mammary glands are without nipples.
Gynaecomastism is found in these animals i.e. male and female both feed their child. Mammary glands are functional in males and females Doth.
Cloaca is present.
Testes in males are situated inside the body (abdominal cavity)
Pinnae are absent and cochlea is less coiled.
Corpus- callosum is absent in brain.
A toothless horny beak is found in adult animals, but teeth are present in child hood.
These are partially homeothermic animals
Members of this subclass are found in Australia, Newguine and Tasmania.
Only one order is included in this subclass.
Order - Monotremata
Connective links between reptiles and mammals.
e.g..
Ornithorhynchus or Duck billed platypus- poison glands are found in male platypus.
Tachyglossus or Echidna or spiny anteater.
Subclass - Theria
These are viviparous animals.
Embryo is attached with uterus of mother by placenta.
Mammary glands with Nipple
Cloaca absent
Testes are situated in scrotal sacs.
Pinnae are present and cochlea much coiled.
Corpus collosum present
Teeth are present
Teeth are found in adult and children both.
Subclass Theria is subdivided into two infra classes
(A) Infraclass - Metatheria or Marsupials
An abdominal pouch called marsupium is found in these animals, in which immature young ones are developed till maturity.
Mammary glands are present and nipples are also found on these mammary glands, these are situated in marsupium.
Penis is bifid, two vagina, two clitoris and two uteri are present in a female animal.
Yolk sac, placenta are found.
Cochlea is more coiled in internal ear.
Teeth are present in adult animals, which are monophyodont and heterodont type.
Corpus callosum is also absent.
Only one order is included in this infraclass.
Order - Marsupialia
Characters like metatheria Animals are ovoviviparous e.g.
Macropus-Kangaroo-Found in Australia only.
Saltatoriall ocomotion (Tail to use as body balance)
Didelphys - Opossum - Found in North America.
Shortest gestation period (12-13 days).
Dasyurus - Tiger cat.
These are true mammals, that give birth to a mature child. A true placenta is found, which is allantochorionic type.
Nipples are well marked in mammary glands.
Uterus and vagina are single i.e. only one uterus and only one vagina are present in a female. Penis simple.
Cochlea is highly coiled.
Corpus callosum is found in brain.
Completely endothermic animals.
Infraclass Eutheria is divided into 16 orders
Order (1): Insectivoral
These are burrowing nocturnal and insectivorous animals.
e.g.
Erinaceous - Jhau - Chuha/Hedge Hog
Sorex - Shrews: smallest mammals size is about 3- inches:
Chhachhunder
Talpa - Mole
Order (2): Dermoptera/Flying lemurs
In this group, all the false lemurs are included, which do not fly.
These are fruit eaters (frugivorous)
e.g.Galeopithecus - Flying lemur.
Order (3): Chiroptera
In this group bats are included which can fly in air.
These are true flying mammals.
Skin between forelimbs and hind limbs is expanded in the form of patagium, it works as wing, which helps in flying.
Testes are inside abdomen.
Ecolocation (Radar system) sensory system. e.g.
Pteropus - Flying fox, It is a fruit eater animal.
Vespertilo - Insectivorous bat, it is also called filtter mice.
Desmodus - Vampire bat, it is a sanguivorous animal
Order (4): Rodentia
It is the biggest order in mammals.
These are small, terrestrial, herbivore or omnivore animals.
Incisor teeth grow continuously in these animals and canines are absent, empty space of canine is called diastema.
e.g.
-
Funambulus - Squirrel
-
Ratus ratus - Rat
-
Hystrix- Porcupine = Sehi = Body hair are modified into quills.
-
Cavia - Guinea Pig
-
Dipodomys - Kangaroo rat - Desert rat (Never drink 1- water)
Order (5): Edentata (Ant - eaters)
These are insectivore animals, tongue of these animals is long, thin and sticky.
Digits are clawed.
Teeth ill developed or absent.
It is the only mammal, which has exoskeleton of bony plates or horny scales.
e.g.
Myrmecophaga - Giant ant eater.
Dasypus or Armadillo - It shows polyembryony (4-8 embryoes)
Bradypus - Slowest animal
Order (6): Pholidota (Scaly ant-eater)
Teeth are absent. Tongue is long. e.g.
Manis/pangolin - Scaly ant eater
Order (7): Lagomorpha
Rodent like mammals
Complete herbivore
Canines absent, diastema is present
e.g.
-
Oryctolagus - Rabbit
-
Lepus - Hare
-
Ochotona - Pika (Tailless)
Order (8): Carnivora
Canines well developed.
Smart, strong and carnivore animals.
Upper last premolar and lower first molar are meant for tearing the flesh these are called carnassial teeth.
Digitigrade locomotion.
Terrestrial carnivores animals are called Fissipedia & Marine carnivores are called Pinnipedia.
Digitigrade animals
e.g.
Canis familiaris - Domestic dog.
Felis domesticus - Domestic cat
Panthera leo - Lion - Lions in Irrlia are found only in Gir forests of kathiawar of Gujrat state.
Panthera pardus - Tendua - Panther.
Pantherd tigris - Tiger - It is the National animal of India.
Acinonyx - Cheetah - It is the extinct animal of India.
Vulpes - bengalneneis - Fox.
Zalopus - Sea lion.
Phoca - Seal.
Herpestes - Mangoose.
Ursus - Bear.
Canis lupus - Wolf.
Order (9): Cetacea
These animals are fish like marine mammals
Hind limbs absent.
Hairs & Pinnae are absent.
Testes found in abodmen.
A thick heat resistance layer of adipose tissue is present just beneath the skin, that is called blubber.
e.g.
Balaenoptera musculus - Blue whale - Found in
Antartic ocean. A horny sheet called of Baleen plate (for filtration) is found in upper jaw instead of teeth.
Milk is squirited to through of baby by the muscle contraction of mother. Retea mirabile is found in thoracic region which helps in respiration in under water.
Phocaena porpoise - Small whale
Orcinus - Killer whale.
Caparea - Pigmy whale.
Physeter - Sperm whale - From its intestine Ambergis is secreted which is used in making perfumes.
Platanista gangatica-Dolphin - It is found in Ganga river.
Order (10): Sirenia
Herbivorous aquatic animals.
Hind limbs absent.
Pinnae absent.
A transverse fin on tail. Big tusk in male.
e.g
Rhytina - Sea cow
Trichechus - Manatee
Halicore - Dugong
Order (11): Tubulidentata
Tubular mouth, Tongue Slender & Protrusible. e.g.
Orycteropus - Aardwrark - It is found in Africa.
Order (12): Proboscida
This order includes .largest and heaviest modern terrestrial animals.
Upper incisors long, tubular form tusks. Canine absent.
Molar teeth are lophodont type.
Hair less, Testis found in abdomen. e.g.
Elephas - Indian elephant
Loxodonta - African elephant, it is largest living land animal.
Order (13): Hyracoidea
Small herbivore animals like rabbit
Plantigrade animals
e.g.Hyrax - It is found in Asia and Africa.
Order (14): Artiodactyla
Stomach is four chambered, it helps these animals in ruminating (Cud-chewing).
All animals are Ruminant except pig and Hippopotamus [Nonruminant). Even toed ungulate animals.
e.g.
Bos indicus - Cow
Bubalus bubalus - Buffalow
Camelus - Camel [RBC nucleated]
Sus - Pig
Capra - Goat
Ovis - Sheep
Bos mutus/Poephagus - Yak
Cervus - Dear
Cameloparculelis - Girrafe
Moschus moschiferus - Musk dear (Smallest RBC)
Order 15: Perissodactyla
Limbs long which have 1 or 3 digits with hooves.
These are fast runners.
Odd toed animals
e.g.
Equus caballus - Horse
Equus asinus - Donkey
Equus hemionus - Indian Donkey
Equus zebra - Zebra
Rhinoceros unicornis - Rhino - Single horn Genda. It is found in Kaziranga National Park Jorhat, Assam. Rhino psosses keratin horn over snout.
Order (16): Primates
Most developed mammals. It includes wise or most intelligence animals e.g. man, monkeys, lemur, apes, gibbons, gorilla, chimpangee etc.
Cerebrum highly advanced.
(a) Prosimians
e.g.
Nycticebus - Lemur
Loris - Loris (tailless)
Tarsius - Tarsier
(b) Simians
e.g.
Macaca mulalta - Rhesus monkey
Hylobates - Gibbon - smallest ape. (found in India) Only ape found in India - Hoolock gibben
Gorilla - Largest ape.
Pan Chmipanzee - Most intelligent in apes.
Oranguttan - Man of forest (found in Indonesia)
Homo-sapiens - Man
Review
Mammalia (mammals): Skin with sweat and milk glands, and with hairy coat that conserves body heat, four limbs having digits armed with claws, nails or hoofs, buccal cavity with thecodont, heterodont, diphyodont teeth, spongy elastic lungs, heart 4 chamered, cerebral hemispheres connected together by corpus callosum, optic lobes divided into four corpora quadrigemina, external ear often with pinna, males with copulatory organ, eggs amniotic, fertilization internal, no larval stage, viviparous, diaphragm between thorax and abdomen, endothermic.
To read more, Buy study materials of Animal Kingdom comprising study notes, revision notes, video lectures, previous year solved questions etc. Also browse for more study materials on Biology here.
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Click Here Know MoreAsk a Doubt
Get your questions answered by the expert for free