Human Reproduction
|
Table of Content |
|
|
How to Define a Reproductive System?
The Human Reproductive System is defined as a collection of Internal and External Organs in humans (including both males and females) that work after puberty for the purpose of producing a new individual.
How do Human Reproduce?
-
The fertilization process in humans takes place internally i.e., Humans are Viviparous. The pre-fertilization processes in humans involves gametogenesis and insemination.
-
The formation of gametes (i.e., the sperm and the ovum produced by two parents) by meiosis is known as Gametogenesis and the transfer of male gametes or sperms into the female Genital Tract is known as Insemination.
-
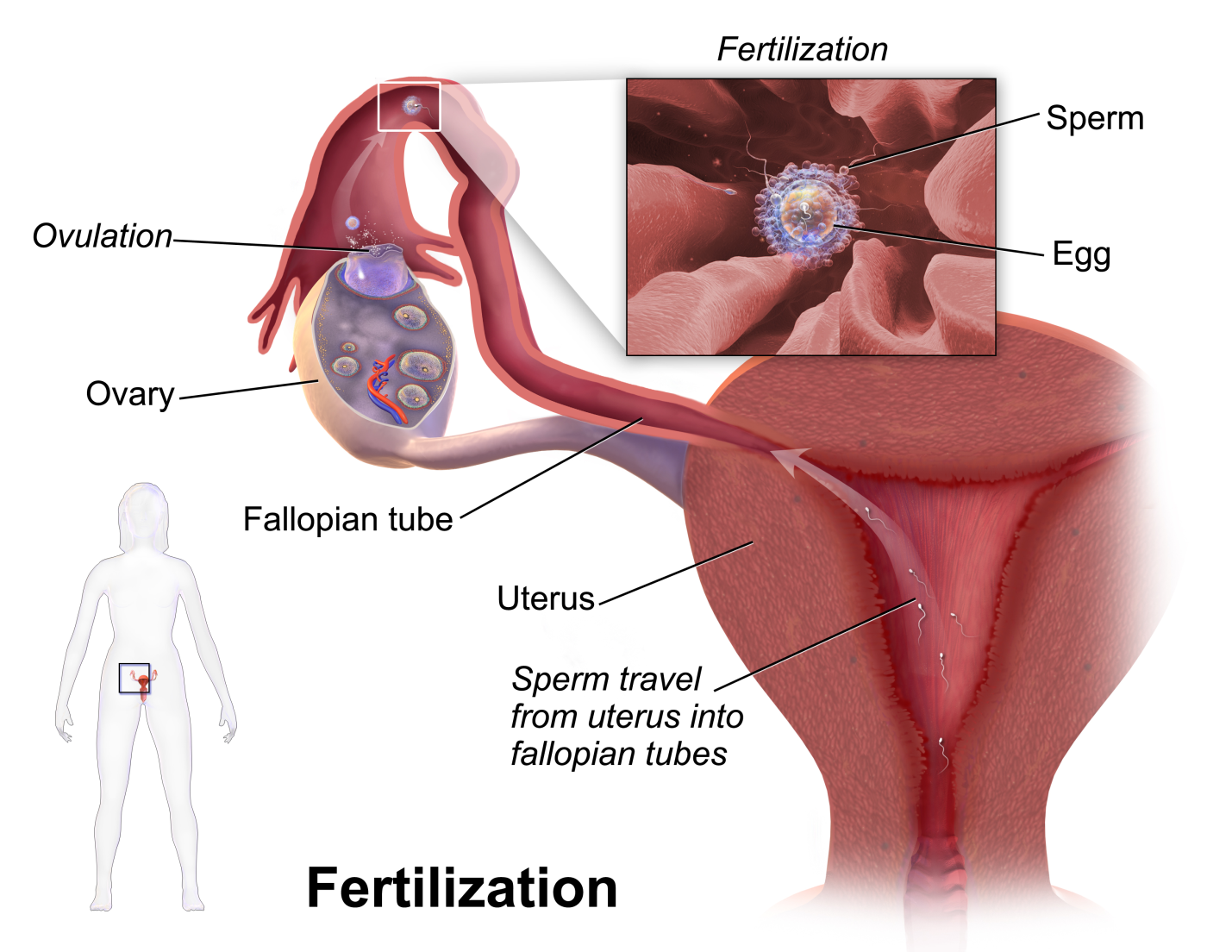
Fertilization is the process of union of male and female gametes within the female's fallopian tubes which results in the formation of zygote.
-
After fertilization, the process of implantation takes place. Implantation means formation of a blastocyst and its attachment to the wall of uterus (also known as Womb).
-
The development of embryo (Gestation) takes place inside the uterus. After gestation period the offspring is delivered.
-
The process of delivery of an offspring is known as Parturition.
-
The offspring produced by sexual reproduction contain genes from both the parents.
In short we can say,
-
Humans are sexually reproducing and the male and female sexes are separate.
-
There is requirement of both male and female for reproduction in human.
-
Male gametes are produced within testes of male while female gametes are produced in ovaries of female.
-
Male semen are ejaculated into vagina of female where sperms (Male Gametes) travel a long distance and reaches up to the female gamete.
-
Fertilization takes place at fallopian tube.
-
A sequence of post fertilization changes leads to birth of infant after 7 to 9 months.
What is the Importance of Reproductive System?
Reproduction is an essential function of all living organisms although unlike other body systems, it's not essential to keeping an individual alive. But, it has an important role in ensuring the survival of the species. It means that all living organisms must reproduce so that their species does not become extinct in future.
“The reproductive system is a collection of internal and external organs — in both males and females — that work for the purpose of procreating (producing offspring’s). Reproduction is a vital function of all living beings and has a important role in the survival of the species”
What is the Definition of a Reproductive Organ?
A reproductive organ is defined as any internal and external organ involved in the process of reproduction.
What is Primary Reproductive Organs?
Primary Reproductive Organs are the organs that produce gametes. They are also called Gonads. The Gonads form a part of the endocrine system and are the primary reproductive organs of both sexes. They contain germ cells that undergo meiosis division and generate gametes.
What are the Examples of Human Reproductive Organ?
|
Female Reproductive Organ |
Male Reproductive Organ |
Functions |
|
Cowper's gland |
Bartholin’s gland |
|
|
Ovary |
Testis |
Production of Gametes |
|
Skene’s gland |
Prostate gland |
Ejaculatory fluid and sensation |
|
Clitoris |
Penis |
Sensation and penetration |
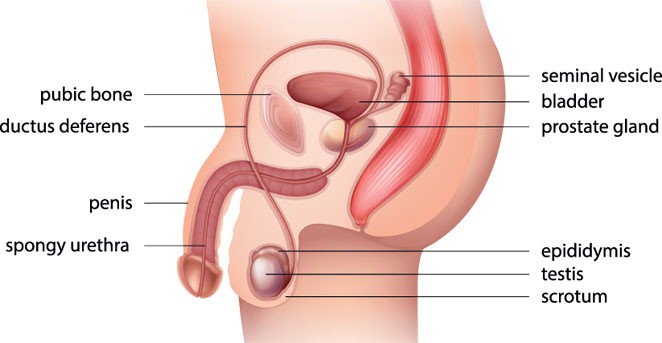
Explain Human Male Reproductive System
-
The Human Male Reproductive System is present in Pelvis Region. It includes a pair of testes, Accessory Ducts, Glands and External Genitalia.
-
Testes are present within a pouch called Scrotum, Hanged to the lower of abdominal cavity.
-
Testes are oval shaped. Length of testis in human adult is about 4 to 5 cm long with width 2 to 3 cm.
-
Testis is made up of about 250 components called Testicular Lobules.
-
Each Testicular Lobule contains 1 to 3 Seminiferous Tubules which are highly coiled and are site of sperm production.
-
The inside lining of seminiferous tubule is made up of male Germ Cells (Spermatogonia) and Sertoli Cells.
-
Formation of sperm takes place by meiotic division of male Germ Cells.
-
Function of sertoli cells is to provide nutrition to the Germ Cells.
-
Interstitial space is the space present outside seminiferous tubules. This contains small blood vessels and also interstitial cells.
-
Interstitial cells are also called Leydig cells.
-
Androgens are the testicular hormones secreted by Leydig cells.
-
Human Male Sex accessory ducts include rete testis, Vasa Efferentia, Epididymis and Vas Deferens.
Why is the Scrotum Situated Outside Body?
Scrotum is Situated Outside the body, so that it’s temperature remains 2 to 3 degrees lower than the normal body temperature. This temperature is necessary to be maintained for genesis of sperms.
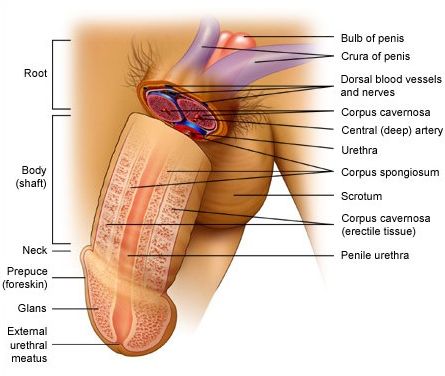
What is Penis?
-
Penis is the male external genitalia i.e. external component of the male reproductive system.
-
Penis is made up of special type of tissue which helps in erection of penis which facilitates insemination.
-
The enlarged end of penis is called the Glans Penis.
-
Glans penis is covered by a loose fold of skin called Foreskin.
What are the male and the female gametes in the humans?
Humans have two particular type of Gametes, the Male Sperm which is capable of Movement (motile) and the female Ovum which do not move (non-motile).
Explain Female Reproductive System
-
The Human Female Reproductive System is located in Pelvic Region. It includes a pair of ovaries, Oviducts, Uterus, Cervix, Vagina and External Genitalia.
-
The Primary Female Sex Organs are ovaries. The Ovaries are located on each side of the lower abdomen. Ovaries produce ovum and secrete hormones like Estrogen and Progesterone.
-
Each ovary is about 2-4 cm in length and is supported by ligaments in order connect to the pelvis wall and uterus.
-
Each ovary is covered by a thin epithelium which encloses the ovarian stroma. The stroma is divided in to two parts Cortex and Medulla. The Cortex is present towards the Periphery and the Medulla is present on the Inner Side.
-
Female accessory ducts constitute of oviducts (also known as Fallopian Tubes), Uterus and Vagina. Each Fallopian Tube extends from the periphery of each ovary and is about 10-12 cm in length.
-
Infundibulum the funnel-shaped part closer to the ovary. The edges of infundibulum have finger like projections called Fimbriae. During ovulation ovaries release ovum into the Fallopian Tubes. The function of fimbriae is to help in collection of the ovum after ovulation.
-
Ampulla is a wider part of the oviduct after the infundibulum. The last part of the oviduct is the isthmus. It has a narrow lumen and joins the uterus or womb. Uterus is the portion where a fetus grows.
-
The shape of the uterus is like an Iinverted Pear. It opens into cervical canal which along with vagina forms the birth canal.
-
The wall of uterus has three layers of tissues namely, perimetrium, myometrium and endometrium. Perimetrium is the membranous covering of the uterus wall, Myometrium is the middle layer made up of smooth muscles and Endometrium is the inner lining of the uterine wall.
-
The female external genitalia include Mons Pubis, Labia Majora, Labia Minora, Hymen and Clitoris.
What are the largest and smallest cells in the humans?
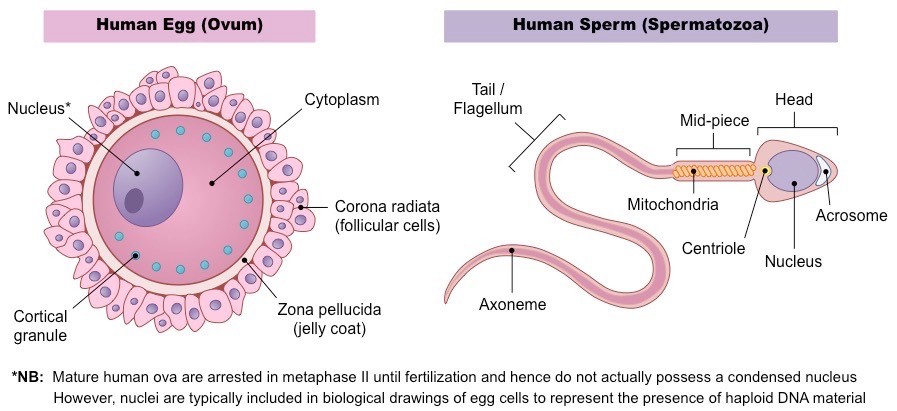
Both the largest and smallest cells in the human body fall into the category of ‘Gametes’. In Humans, Male Gametes are Sperm Cells and female gametes are Egg Cells or Ova. The Human ovum is roughly 1 mm across and is the largest human cell. The male equivalent of the female gamete, commonly known as the Sperm Cell, or Spermatozoon, is only 60 µ in length. It is not visible to the naked eye and is the smallest human cell.
What are Gonads?
The organs that produce gametes are called Gonads. The Gonads form a part of the endocrine system and are the primary reproductive organs of both sexes. They contain germ cells that undergo division and generate gametes.
What are the male and the female gonads in the humans?
In humans, the male gonads are the testicles and the females gonads are the ovaries.
How are Gametes Produced in Human?
-
Gametogenesis is the name given to the process of gamete production. In Humans the process of formation of male and female gametes is known as Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis respectively.
-
The organs that produce gametes are called Gonads or Primary Sex Organs. E.g. testes in males and ovaries in the females.
-
In testis, the germ cells begin to divide at puberty due to increase in the release of Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) and form sperms. This process is also called Spermatogenesis.
-
In the inside wall of seminiferous tubules the diploid spermatogonia or primary spermatocytes multiply and increase in number by mitotic division.
How are Sperms Produced?
-
Spermatogenesis starts at puberty.
-
Sperms are produced in testis by immature germ cells known as Spermatogonia.
-
The spermatogonia are present on the inside wall of seminiferous tubules.
-
Spermatogonia multiply by mitotic division.
-
Each spermatogonium is diploid and contains 46 Chromosomes.
-
Some of the spermatogonia undergo meiosis periodically and are called Primary Spermatocytes.
-
Primary spermatocytes undergo meiotic division to form two equal, Haploid Secondary Spermatocytes.
-
Secondary spermatocytes have only 23 Chromosomes.
-
The secondary spermatocytes undergo 2nd Meiotic division and form four equal, haploid cells known as Spermatids.
-
Spermatids are converted to spermatozoa which are also called Sperms.
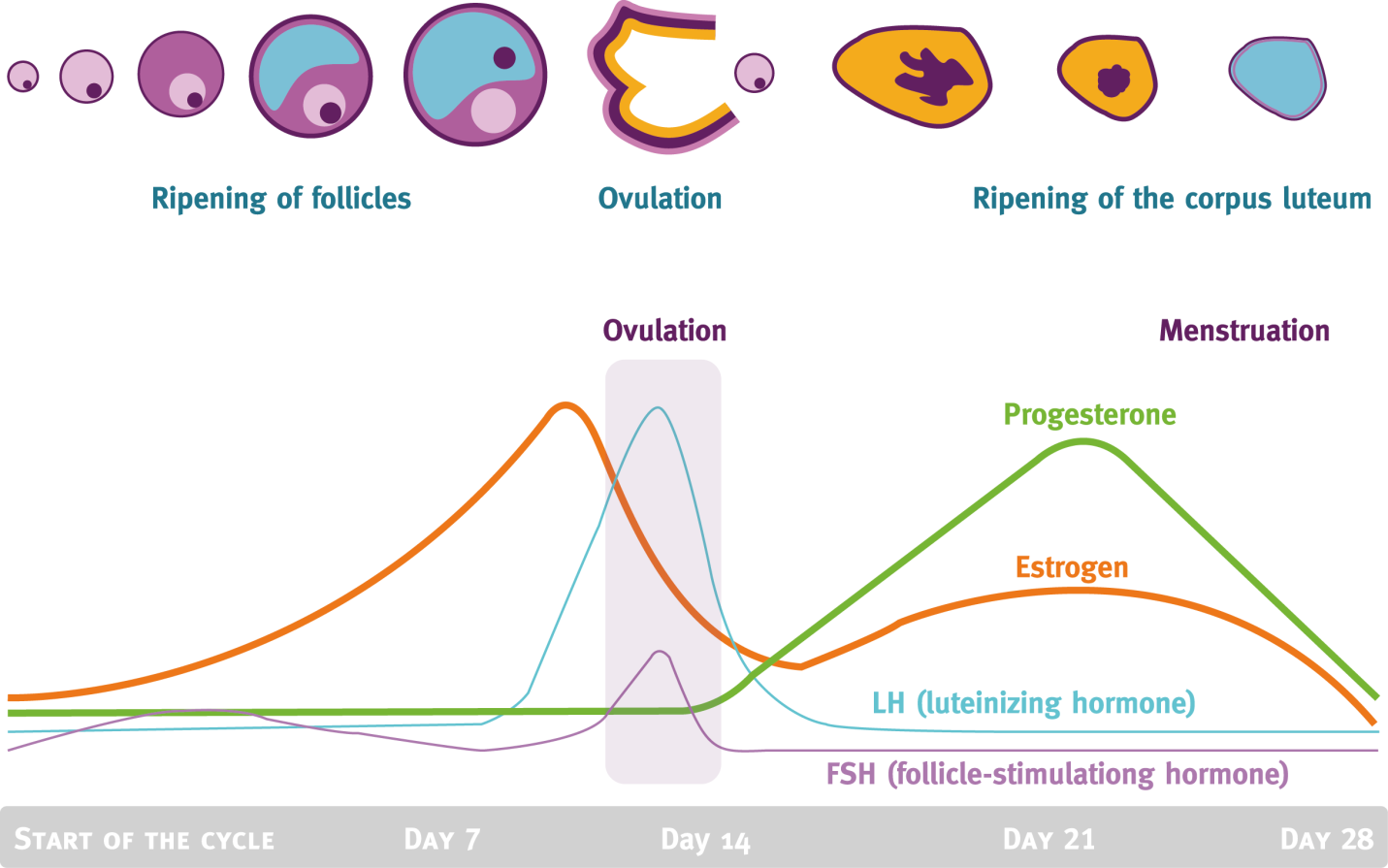
What is Menstrual Cycle?
-
Menstruation, sometimes called Period, happens when the lining of the womb sheds and red blood like material flows out of the women's vagina.
-
Menstruation usually occurs once in a month (approx 28 days) in women.
-
Menstruation signals that a woman is releasing eggs that can be fertilized.
-
The lining of the womb grows to prepare for supporting the growth of a baby.
-
If the egg is not fertilized in that month, the womb will shed its lining and begins growing a new.
-
The Uterine (menstrual) cycle is a series of cyclic changes that the uterine endometrium goes through each month in response to changing levels of ovarian hormones in the blood.
-
The menstrual phase takes place on days 1–5 typically, and is the time when the endometrium is shed from the uterus i.e. the old functional layer is sloughed off.
-
The Proliferation Phase (days 6–14) is the time in which the endometrium is rebuilt, once again becoming velvety, thick, and well vascularized i.e. a new functional layer is formed in the uterus.
-
The Secretory Phase (days 15–28) is the phase in which the endometrium prepares for implantation of an embryo.
Why menstrual cycle is required?
-
It is required to wash out the ruptured follicles.
-
Menstrual cycle has role in the pregnancy.
-
Pregnancy occurs when conception occurs during the fertile phase of the woman.
-
After menses 5-7 days are called Safe Period.This is the phase when the conception is least likely to occur.
 Structure of Human Sperm
Structure of Human Sperm
-
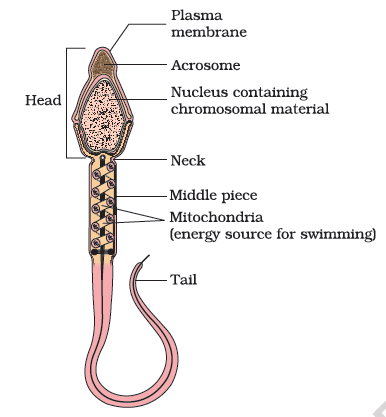
Sperm has a microscopic structure which has a head, neck, a middle piece and a tail.
-
A plasma membrane covers the whole body of sperm.
-
The sperm head has an elongated nucleus which is haploid.
-
The anterior portion of nucleus is covered by a cap-like structure, acrosome.
-
The acrosome of sperm is filled with enzymes.
-
These enzymes help in fertilization of the ovum.
-
The middle piece of sperm possesses numerous mitochondria, which produce energy for the movement of tail that facilitate sperm motility essential for fertilization.
What is Fertilization?
-
Fertilization is the process of fusion of a sperm with an ovum.
-
For fertilization, a sperm makes contact with the zona pellucida layer of the ovum and induces changes in the membrane that block the entry of additional sperms.
-
A diploid zygote is formed by mitotic division after fertilization.
-
Zygote moves through the isthmus and the mitotic division called cleavage starts with the movement of zygote towards uterus, leads to the formation of blastomeres (8-16 cells).
Frqequecy Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the human reproductive system?
Sol: It is collection of internal and external organs in humans (including both males and females) that work after puberty for the purpose of producing a new individual.
Q2. What is the name of the female reproductive cell?
Sol: Ova is the name used for female reproductive cell.
Q3. Are baby girls born with all their eggs?
Sol: Here egg represents the female gamete Which is present in the baby girl even at the time of her birth. Only maturation of these egg occurs at the age of puberty.
Q4: Where is the female reproductive system located in the body?
Sol: Female reproductive system is located in the pelvic region.
Watch this Video for more reference
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More