Be the first to read about ctenophores, aschelminthes & Platyhelminthes as explained by Biology Expert
I believe you always like reading my articles! Thank you so much for the appreciations guys! Because of the student’s demand; I am writing one more article. Few of my articles are based upon biological classification. Here again, I am going to tell you those categorization, which I haven’t told you before.
All of my words are going to be related to ctenophores, aschelminthes (nematoda) & Platyhelminthes. They all fall under the category of non-chordates in Kingdom Animalia. Don’t worry! It’s very easy J
You can see the classification of Animal Kingdom in this flow chart. Look it closely, because I am going to tell you now features of them.
You need to drink this classification! Guys, move cursor now as you are going to get very important information!
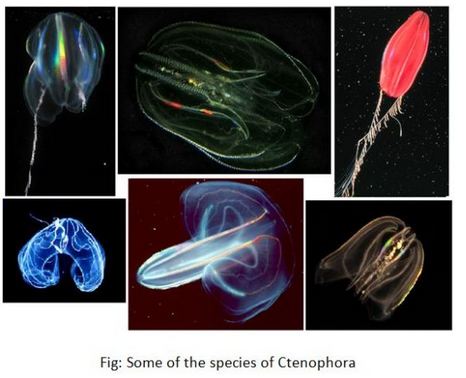
Ctenophora – (Gk. Ktene- comb, phors – bearing, Pronounced as – teen-o-four)
These are the comb jellies. Ctenophores are specifically marine organisms. Probably, there are 100-150 species of them. They can probably be the common members of planktons. Some of the small sized ctenophores are even invisible. Various kinds of ctenophores include coastal, benthic, oceanic & very beautiful bioluminescent one. Some of their special features are
- Ctenophores are carnivores.
- Their larval stage is
- Well-developed sub epidermal nerve net is present.
- Digestive system is complete with separate mouth & anal opening.
- Mostly sexual reproduction occurs in them (as hermaphrodite) but occasionally sexual reproduction also occurs.
- Body is variable. It can be multicellular with tissue level or organ level of organization.
- Combs which are actually plates of cilia help them to swim.
- They may feed upon each other as well.
- They use sticky tentacles & oral lobes to capture the prey.
- Ctenophores have bilateral symmetry.
- Some of the examples are – Hormiphora, cestum, beroe, pleurobrachia etc.
- They are divided in to two classes viz. tentaculata & nuda.
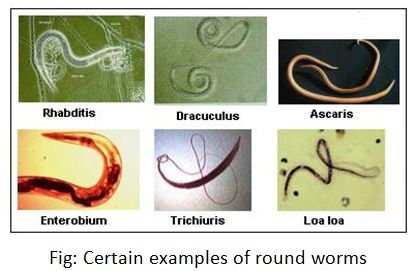
Aschelminthes – Also known as nemanthelminthes (Gk. nema – thread, helmin – worm), nematode or roundworm.
They are microscopic & worm like invertebrates. All organisms in this category are put together because of the presence of the pseudocoelom in it. Their body cavity (coelom) is quite different.
They do not have any evolutionary relationship with each other. They are related to other phylum as well in relation to their other features.  Certain characteristics of them are
- Their body is unsegmented & is wrinkled. Annulation is present in specifically marine species.
- Their body doesn’t consist of any pigment & that’s why it is either colorless or pale in color.
- Nematodes have long, elongated & fusiform body.
- They are usually parasitic.
- Respirations in nematodes occur simply by diffusion.
- They organization is at the organ level.
- Symmetry is bilateral with triploblastic body layers.
- Digestive system is complete (separate mouth & anal opening).
- Distinct male & female sexes are present.
- Females are usually longer then male.
- Nerve ring & longitudinal nerve cords constitute the nervous system.
- Body walls of nematodes are made up of cuticle, epidermis & musculature.
- Four larval stages are present in which third one is infective.
- Some of the examples are –
- They are classified into 2 classes viz. Aphasmidia & phasmidia.
- Some of the examples are – Ascaris lumbricoidis, Wuchereria, loa loa, trichinella, enterobius, drancunculus etc.
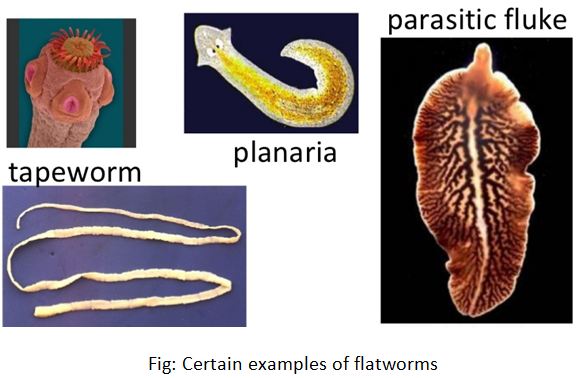
Platyhelminthes – (Gk. Platys – broad/flat, helmin – worm)
Flatworms include about 13000 species. They are soft bodied invertebrate animals. Flatworms are basically dorso-ventrally flattened organisms. I am expecting, you are grasping every information that I am telling you. Now, again we are taking a look to the features of platy-helminthic organisms. Which are
- Their body is covered with a cuticle.
- They are free living & primarily they are aquatic.
- They have complex life cycle which involve multiple hosts.
- Cross & internal fertilization occur between hermaphrodite Asexual reproduction occurs by regeneration where they just grow several parts of the body.
- Flatworms have ladder like nervous system.
- Flatworms show bilateral symmetry.
- Excretion occurs by protonephridia (also known as flame cells). It helps in osmoregulation as well.
- They are classified into 3 classes viz. Turbelllaria, trematoda & cestoda.
- Some of the examples are – Dugesia, fasciola, Schistostoma, polystomum, taenia, echinococcus etc.
There is a greater than great chance that you are going to have certain questions in your exam from these topic. Don’t be afraid! Study well! Have any doubt? Post it over this link. It’s going to be answered.
If you want more information over the same, just jump in here & here.
If you remember me; I am Anjali Ahuja, Your Biology Educator. Along with askIITians, we have created a good study material for you. I am sure you are going to like it. See it here.