Nail down the reactions associated with Benzene on your fingertips!
 So planning to study Benzene ?
So planning to study Benzene ?
The monster?
So how many hours do you expect to spend on it and are you actually hopeful of being successful in memorizing it completely? Well, I know the response of many of you! Organic Chemistry in itself is like a ghost and then learning so many reactions… oh my God! But, here we come to your rescue! I am sure this piece would prove to be very useful to you and will help you memorize the reactions related to benzene very easily and quickly!
Organic chemistry is generally considered to be a difficult branch of chemistry. This branch deals with the study of structure, properties and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials that mainly include matter in its various forms containing carbon atoms. Various physical and chemical methods are used to determine the chemical composition and constitution of organic compounds and materials.
There are many carbon compounds that are human-made or synthetic. For chemists, these too constitute the organic compounds. Plastics are organic, and so are most synthetic wonder drugs, as far as chemists are concerned. They are organic because they are carbon-based. Even the synthetic fertilizers are also considered organic because they are made of molecules mainly comprising carbon atoms.
Various methods are used to assess the chemical reactivity and study their physical and chemical properties. This mainly aims at recognizing the behavior of the organic matter not only in its pure form, but also in solutions, mixtures and fabricated forms. A wide array of chemicals is studied in organic chemistry including hydrocarbons which are compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen as well as compositions based on carbon but containing other elements.
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. Its molecule comprises of 6 carbon atoms connected in a ring with an attached hydrogen atom with every carbon atom. Benzene comes under the class of hydrocarbons because its molecules contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms. Benzene, a component of crude oil, is also a rudimentary petrochemical. It is an aromatic hydrocarbon which is a cyclic hydrocarbon with a continuous pi bond. Some of the basic properties of Benzene are listed below:
- It is abbreviated as Ph
- It is colorless
- It is highly flammable liquid with a sweet smell
- A vital component of gasoline because of its high octane number
- Used as a precursor to heavy chemicals like ethyl benzene and cumene
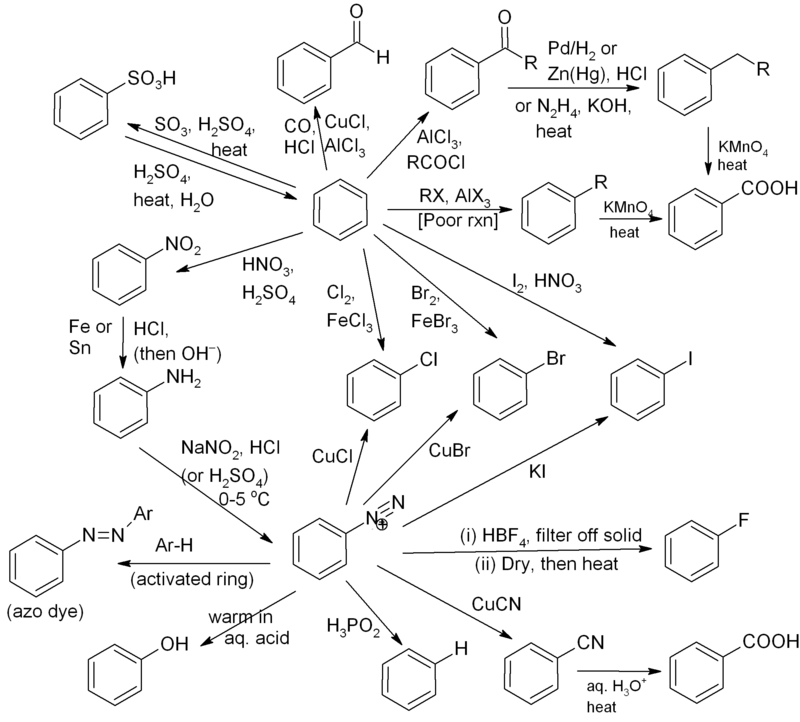
We now discuss the formation of various products of benzene. Generally, it is considered to be very tough to memorize all the products as there are too many compounds and moreover the reactions are also very complicated. We provide you a very easy method of absorbing the products formed by benzene in a diagrammatic way.
Given below is the mind map of benzene
Mind -Map is primarily used to visualize the outline information. It is the simplest way of memorizing the reactions generated from a compound. The compound to be discussed is placed at the center and the various other compounds which are produced or are involved in the reactions of the major compound are connected to it with the help of arrows.
Here, benzene or Benzenediazonium salt is positioned at the center and the other compounds are connected to it through the spider web diagram. It exemplifies the various products along with the basic conditions and reagents used in the reactions besides benzene. The mind map shows the formation of the major products in a web diagrammatic way. The reactions describing the formation of various products from benzenediazonium salt have also been included. In fact, the formation of Benzenediazonium salt from benzene has also been depicted in the mind map.
Tips for learning the mind map
Mind Map itself is a very easy way of picking up the reactions associated with benzene. We further help you out in learning this mind map. What you can do with this mind map is:
- You just have to put this on your table
- Just place it on your board
- Just place it on your bedroom wall
- Just place it on your Mirror (For Girls)
- Just place inside your bathroom wall (For boys)
In fact, you may place it anywhere as per your convenience. Now after placing it, just view it every morning. Actually, if it is placed at a place you visit many times in a day you will be able to grasp it even more quickly. And you will see that without putting in any extra efforts you have prepared one of the toughest topics of organic chemistry. This is the fastest and the easiest way of memorizing the reactions, products and reagents.
BONDING IN BENZENE
The Kekulé structure for benzene, C6H6
What exactly do we mean by the Kekulé structure?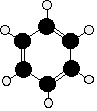
Kekulé was the first to suggest a sensible structure for benzene. The carbons are arranged as shown in the figure. It is clear that they form a hexagon. He also suggested alternating double and single bonds between them. Each carbon atom has hydrogen attached to it. This diagram is often simplified by leaving out all the carbon and hydrogen atoms!
 In diagrams of this sort, there is a carbon atom at each corner. In order to work out the number of hydrogen attached to it you will have to count the bonds leaving each carbon.
In diagrams of this sort, there is a carbon atom at each corner. In order to work out the number of hydrogen attached to it you will have to count the bonds leaving each carbon.
In this case, each carbon has three bonds leaving it. Because carbon atoms form four bonds, that means you are a bond missing – and that must be attached to a hydrogen atom.
Issues with the Kekulé structure
Although the Kekulé structure was a very good effort, there are serious problems with it . . .
Problems with the chemistry
Because of the three double bonds, one expects benzene to have reactions like ethene – only more so!
Ethene undergoes addition reactions in which one of the two bonds joining the carbon atoms breaks, and the electrons are used to bond with additional atoms. But this rarely happens in the case of Benzene. Instead, it usually undergoes substitution reactions in which one of the hydrogen atoms is replaced by something new.
Issues with the shape
Benzene is a planar molecule i.e. all its atoms lie in one plane. But in this respect the Kekule structure is fine. The issue is that the C-C single and double bonds are of different lengths.
C-C    0.154nm
C-C      0.134nm
Remark: “nm†stands for nanometre , which is 10 -9 metre.
Hence, by this it follows that the hexagon would be irregular had it been in accordance with the Kekule structure, with alternating shorter and longer sides. But in case of real benzene, the shape is a perfectly regular hexagon.
Friends, this is the just the beginning! Gear up yourselves to be masters of organic chemistry with askIITians as we will continue helping you out on various other compounds of organic chemistry!
Feel free to contact us via contact us form !
This post was published by Aditya Singhal, co-founder of askIITians.