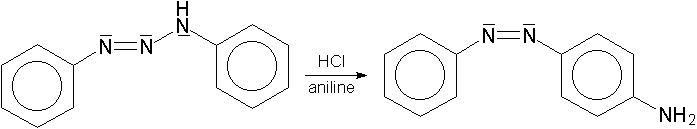
Diazonium coupling is decisively influenced by the pH value of the reaction mixture. Strong basic solutions must be prevented, as diazonium cations are stable only under acidic and moderately basic conditions. Diazonium coupling in connection with amines is carried out in faintly acidic solutions in order to ensure an as high as possible diazonium cation's as well asunprotonatedaromatic amine's concentration. The result of low pH values is a largely protonated and, thus, deactivated aromatic amine, while higher pH values would cause lower diazonium cation concentration.