Oxidation Reduction
Table of Content |
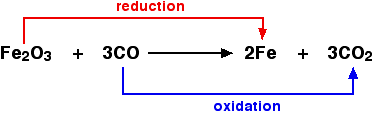
Oxidation and Reduction in terms of oxygen transfer
Fig. 1. Oxidation and reduction in terms of oxygen transfer
When oxidation and reduction occurs together, this is known as Redox Reaction.
Oxidation and Reduction in terms of Hydrogen Transfer
-
Oxidation involves the loss of hydrogen.
-
Reduction involves gain of hydrogen.
Oxidation and Reduction in Terms of Electron Transfer
-
Oxidation is defined as loss of electrons.
-
Reduction is defined as gain of electrons.
The easiest method to learn oxidation and reduction is LEO-GER/OIL-RIG system.
OILRIG stands for Oxidation Is Loss and Reduction Is Gains. IN ELECTRONS.
LEOGER (leo the lion says grr) stands for Loss of Electrons = Oxidation while Gain in Electrons = Reduction.
Fig. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of electron transfer
Oxidizing and Reducing Agents
Oxidizing agent is a substance that oxidizes another substance but itself gets reduced. For example, Sulphuric acid, oxygen, ozone etc.
Reducing agent is a substance which reduces another substance but itself gets oxidized. For example, hydrogen, lithium, iron, zinc etc.
Fig. 3. Oxidizing and Reducing agents
Balancing Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
The method used to balance the redox reactions is called the Half Equation Method or ion electron method. Each equation is balanced by adjusting coefficients on both the sides, that is, reactant as well as product side.
This can be explained using an example given below-
Cu+(aq) + Fe(s)→Fe3+(aq) + Cu(s)
-
Separate the reactions into half reactions
Cu+(aq) + e−→Cu(s)
Fe3+ (aq)+3e−→Fe(s)
3Cu+(aq) +3e−→ 3Cu(s)
Fe(s) →Fe3+(aq) +3e−
-
Add both the equations and cancel the number of electrons and balanced equation will be-
3Cu+ (aq)+ Fe(s)→3Cu(s)+ Fe3+ (aq)
Oxidation Number Method
This can be explained step by step wise using an example:
Step 1
The skeleton equation is:
Zn + HCl → ZnCl2 H2
Step 2
Oxidation number of various atoms involved in the reaction:
0 + 1 – 1 + 2 –1 0
Zn + HCl → Zn Cl2 + H2
Step 3
The oxidation number of zinc has increased from 0 to +2 while that of hydrogen has decreased from +1 to 0. However, the oxidation number of chlorine remains same on both sides of the equation. Therefore, zinc is reducing agent while HCl is oxidizing agent in reaction:
Step 4
The increase and decrease in oxidation number per atom can be indicated as: O.N. increases by 2 per atom
Step 5
The increase in oxidation number of 2 per atom can be balanced with decrease in oxidation number of 1 per atom if Zn atoms are multiplied by 1 and HCl by 2. The equation will be:
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Watch this Video for more reference
More Readings