Thermodynamic Principles of Metallurgy
Table of Content |
Thermodynamic Principles
Thermodynamic Principles are applied to the ore extraction process. Gibbs energy is the most important term used to explain the thermodynamic principle. Gibbs equation is given below:
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
ΔG is the change in the Gibbs energy
ΔH is the change in the enthalpy.
T is the temperature
ΔS is the change in the entropy.
K is the equilibrium constant.
R is the universal gas constant
Ratio of equilibrium concentrations of reactants and products will give equilibrium constant K. When a reaction moves from reactants to products, products are present in excess and equilibrium constant will be positive. But when reaction moves from products to reactants, equilibrium constant will be negative.
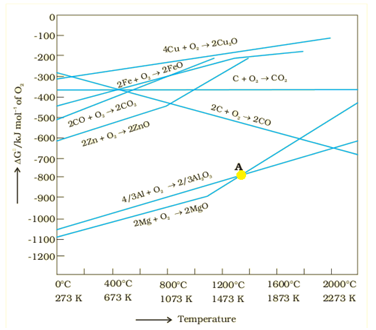
Ellingham Diagram
It is a graphical representation of Gibbs energy. These diagrams are used for finding the choice of reducing agent in the reduction of the oxides. These are used to find out the feasibility of thermal reduction of an ore.
Fig. 1. Ellingham Diagram
As we know, during reduction, the oxide of a metal decomposes,
MxO(s) → xM (solid or liq) + 1/2 O2 (g)
If reduction is being carried out then,
C(s) + 12 O2(g) → CO(g)
CO(g) + 12 O2(g) → CO2(g)
If carbon is taken, there may also be complete oxidation of the element to CO2:
½ C+1/2O2 → 1/2CO2
Limitations of Ellingham Diagram
-
It does not give any information regarding the kinetics of the reduction process.
-
These diagrams believe that reactants and products are in equilibrium, but this is not always the case.
Watch this Video for more reference
More Readings
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Click Here Know MoreAsk a Doubt
Get your questions answered by the expert for free