Biodegradable Polymers
Table of Content |
Biodegradable Polymers are those polymers which degrades after their use and breakdown into some natural products such as water, biomass, inorganic salts etc. They can be natural as well as synthetic polymer.
Non-Biodegradable Polymers do not breakdown after their use. They persist in the environment and brings harm to it. For Example: Polythene.
Fig.1. Biodegradable polymers and their sources
Some examples of biodegradable polymers are as follows:
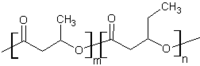
- Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) or PHBV is a biodegradable, biocompatible polymer. It is produced naturally by bacteria. It is used in medical implants, repairs, orthopedic devices etc. 3-hydroxybutanoic acid and 3-hydroxypentanoic acid polymerizes to form PHBV
- Nylon 2–nylon 6 is a copolymer of glycine and amino caproic acid.
- Polyglycolic Acid is a thermoplastic polymer formed by poly-condensation of Glycolic Acid. It has importance in biomedical fields such as implants, pins, rods and plates etc.
- Polylactic Acid is obtained from natural sources such as corn starch, sugarcane etc. It is used in 3D printing, film and sheet casting.
Is Polyester Biodegradable?
No, Polyester is not biodegradable.
Biomedical Applications of Biodegradable Polymers
-
These polymers are used for manufacturing of implants such as rods, pins etc.
-
Orthopedic devices are made up of biodegradable polymers.
-
Oxygen transport membrane is made from biodegradable polymers.
-
Surgical sutures are made from biodegradable polymers.
Advantages of Biodegradable Polymers
-
Environment friendly
-
Biocompatible
-
They are renewable
-
Non-toxic
Watch this Video for more reference
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More