Chemicals in Food
Table of Content |
Today’s science has developed modern food processing and production methods that no doubt is one of the greatest inventions of human mankind. However that also have opened major flaws and negative exposure to environment by carcinogens (endocrine-disrupting) compounds.
Fertilizers and Pesticides used on crops, antibiotics used on poultry, and hormones given to cattle for milk expose consumers indirectly to contaminants that gradually becomes a part of our body. Some of these exposures may have deadly results.
Our ancestors were easy go as they didn't have chemically treated food and chemically enhanced kitchenware and their diets and cooking practices exposed them to fewer toxic hazards.
What is a Food Additive?
All those chemicals which are added to food to improve its keeping qualities, appearance, taste, odour, and nutritive value are called as Food Additives.
Some important food additives are:
-
Food colours
-
Flavours and sweetener
-
Fat emulsifier and stabilising agents
-
Food improvers- anti staling agents and bleaches
-
Antioxidants
-
Preservatives
-
Nutritional supplements such as minerals, vitamins and amino acids
Except for the nutritional supplements, none of the above additives have nutritive value. These are added either to increase the shelf life of stored food or for the cosmetic value (taste, appearance etc.). Details of each class are described below:
-
Food Colours: To give food a specific colour, food colours are used. Actually food colours are dyes or pigments that impart its colour to the food when mixed with the food.
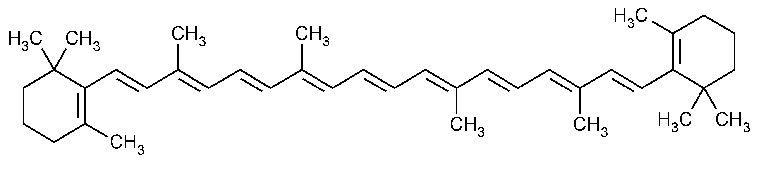
Example: Beta-carotene is an organic food colour which is used to give margarine a yellow colour.
Fig. Structure of Beta-Carotene
-
Flavours and Sweeteners or Artificial Sweeting Agents: The agent which provides sweetness to the food is called Artificial Sweeting Agents. Sucrose and Fructose are most widely used natural sweeteners but it causes tooth decay and obesity. Hence, now days many peoples are taking artificial sweeteners as it doesn’t cause any harm to the body.
Some Artificial Sweeteners are given below:
-
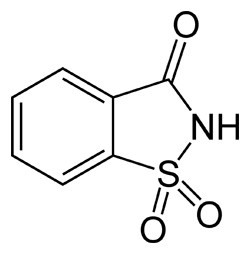
Saccharin: Its IUPAC name is o-sulphobenzimide. It is most popular artificial sweeteners, it is insoluble in water, therefore, it is sold in the market as its sodium or calcium salt. It is about 550 times sweeter than sugar; it is non-bio-degradable and does not have calorific value of food. It is mostly taken by the Diabetic patients.
 |
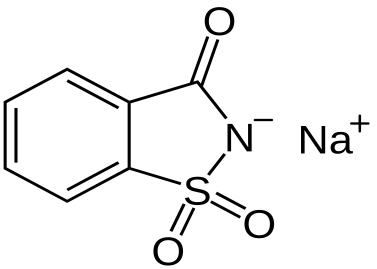 |
| Fig. Structure of saccharin | Fig. Structure of sodium salt of saccharin |
-
Aspartame: It is the most widely used sweetener. It is the methyl ester of the dipeptide derived from phenylalanine and aspartic acid. Aspartame is 100 times sweeter than sucrose. It decomposes at cooking or baking temperature and hence can only be used in cold foods and in soft drinks. The persons suffering from phenylketone urea disease cannot use aspartame because their metabolism convert the aspartame to phenylpyruric acid and it is very harmful to infants as it causes brain damage and mental retardation.
Fig. Structure of Aspartame
-
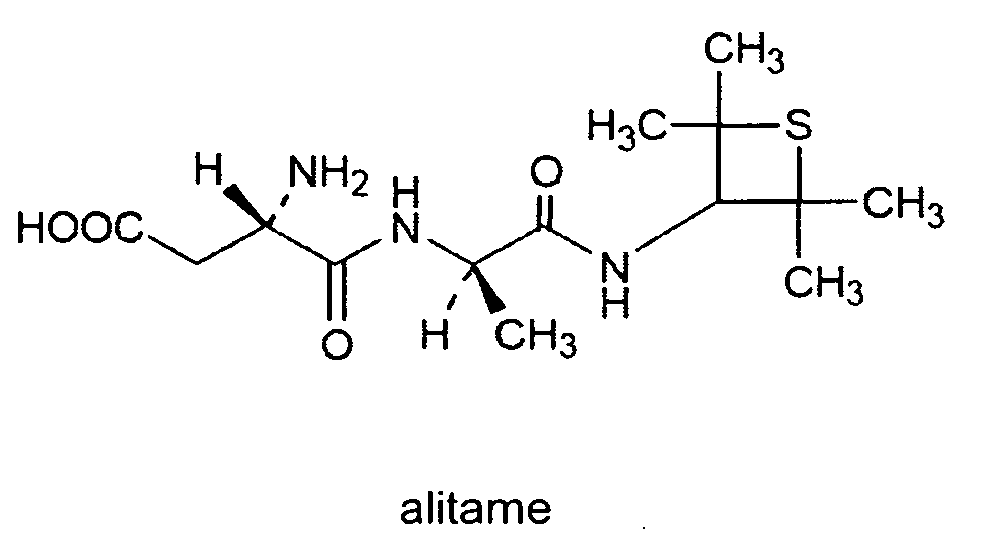
Alitame: It is also similar to aspartame. It is about 2000 times sweeter than sucrose. However, it is a high potency sweetener and it is difficult to control its sweetness to the food.
Fig. Structure of Alitame
-
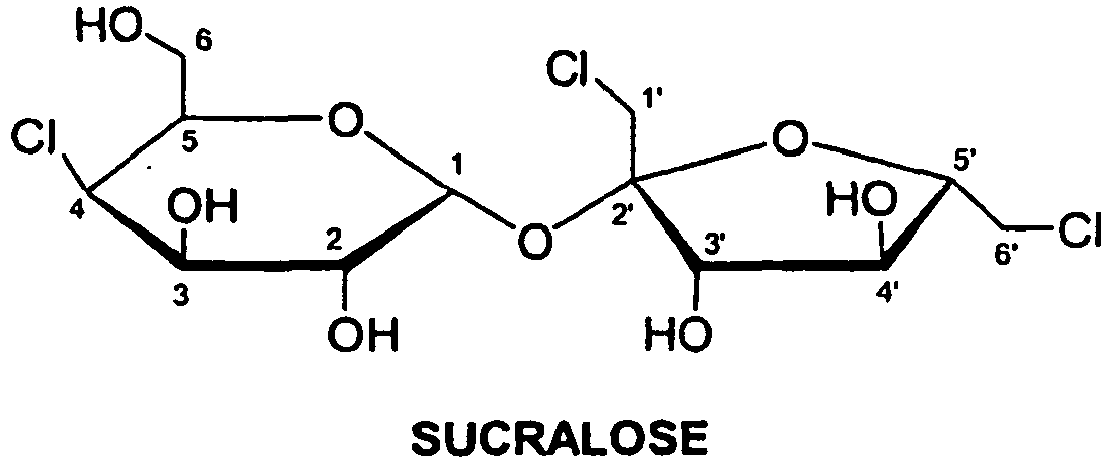
Sucralose: It is a trichloro-derivative of sucrose. It looks and taste like sucrose and is stable at temperature used for cooking. It is about 600 times sweeter than sucrose and it also doesn’t cause any tooth decay or disease.
Fig. Structure of sucralose
-
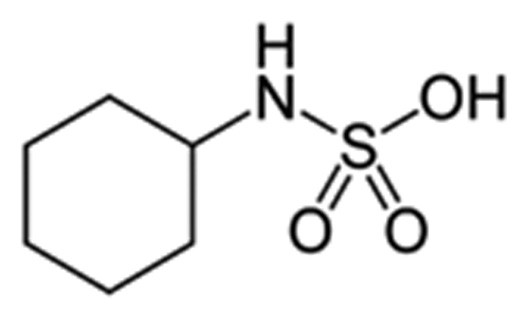
Cyclamate: It is about seven times sweeter than sucrose. A common formulation containing 10:1 mixture of cyclamate and saccharin is found to be more sweeter than either of the two individual compounds.
Fig. Structure of Cylamate
-
Fat Emulsifier and Stabilising Agents: These agents are added to the oils so that oil can easily mix with water, it also prevents the growth of moulds.
-
Flour Improvers: They are added to the flour to improve it baking functionality.
-
Antioxidants: These substances are used to prevent oxidation inside the packed food. So that it can last for long time.
-
Preservatives: Chemical substances which are used to protect food against bacteria, yeast and moulds are called Preservatives. They are classified into two group: Class-I and Class-II respectively. Class-I preservatives include table salt, sugar and vegetable oils. Some common preservatives of class-II are given below:
-
Sodium Benzoate: It is the most commonly used preservative. It is used in soft drinks and acidic foods.
-
Sodium Metabisulphite: It is used as a preservative in foods like jams, pickels, squashes etc.
-
Sorbic Acid and its Salts: Sorbic acid is highly effective in inhibiting the growth of yeasts and moulds. It is used for controlling the growth of yeasts and moulds in several foods like cheese, baked food, certain meat etc.
What is BHT? What are its Ingredients?
BHT stands for ‘Butyl hydroxytoluene’. It is a fat-soluble compound which is used to preserve cosmetic and food to slow down the rate of their autoxidation. As autoxidation, can change the taste and colour of the compounds. It is also used in pharmaceuticals, rubber etc.
Fig. Structure of BHT
Chemicals in Food – Harmful for us: There are certain harmful chemicals which are commonly found in our food and can causes serious trouble to our health. Some of them with descriptions are given below:
-
Bisphenol A: It is commonly found on the plastic containers in which we keep our food and its presence is prone to cause breast cancer.
-
Vinyl Chloride: The polymer of Vinyl chloride (Poly vinyl chloride) is used in food packaging and its presence is carcinogenic to human beings.
-
Pesticides: Now a days, farmers use pesticides for killing harmful organism to protect their crops. The harmful content of the pesticides is absorbed by the crop and the land water, which is very harmful for human consumption. It is carcinogenic to human and even causes cancer.
Watch this Video for more reference
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Click Here Know MoreAsk a Doubt
Get your questions answered by the expert for free