Geometric Progression (G.P.)
Table of contents |
Meaning of Geometric Progression (G.P.)
Geometric Progression is the sequence of numbers such that the next term of the sequence comes by multiplying or dividing the preceding number with the constant (non-zero) number. And that constant number is called the Common Ratio. It is also known as Geometric Sequence.
a, ar, ar2, ar3, …, arn
-
The first term of the sequence is called the Initial Term or the scale factor which is denoted as ‘a’.
-
The ratio of a term to its next term of the sequence is called the Common Ratio, which is denoted by‘r’.
-
The general term that is, the nth term of the geometric progression with the initial term ‘a’ and the common ratio ‘r’ is as
an = a.rn-1
Example
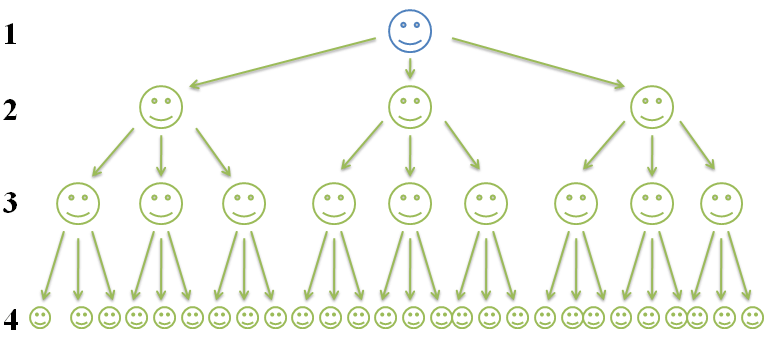
Consider the above figure:
Here the sequence is given as

Let’s check the value of the 4th term using the nth term formula.

It is given in the above figure that the 4th term is 1/16
Finite and Infinite Geometric Progression
The geometric progression with a limited number of terms is called Finite Sequence. It has a last term.
Example
1, 2, 4, …, 64
This is a finite sequence with a =1 and r = 2
The geometric progression with unlimited number of terms is called Infinite Sequence. It does not have a last term.
1, 3, 9, 27, …
This is an infinite sequence with a = 1 and r = 3
How do you find the common ratio of a Geometric Sequence?
The common ratio is the ratio of the term of the geometric sequence to its previous term. And it is denoted by “r”.
Sometimes we need to calculate the common ratio of the sequence. So to find the common ratio, we need to take the ratio of the terms with their preceding term.

Example
What is the common ratio of the sequence?
3, 6, 12, 24, …
Solution:
Given
a1 = 3
a2 = 6
a4 = 24

Hence the common ratio is 2.
How can we check whether the sequence is geometric sequence or not?
If we need to check whether the sequence is geometric sequence or not, we can use the formula of common ratio for this.
Example 1
Check whether the sequence is geometric sequence or not?
4, 8, 24, 96, …
Solution:
Given
a1 = 4
a2 = 8
a3 =24
a4 = 96
Let’s find the common ratio of the given sequence.

Here the ratio of all the terms with their preceding term is not constant, so this is not a geometric sequence.
Example 2
Check whether the sequence is geometric sequence or not?
7, 21, 63, 189, …
Solution:
Given
a1 = 7
a2 = 21
a3 = 63
Let’s find the common ratio of the given sequence.

Here the ratio of all the terms with their preceding term is constant that is, 3, so this is a geometric sequence.
Behavior of Common Ratio
It depends upon the value of the common ratio that the geometric progression is increasing or decreasing.
-
If the common ratio ‘r’ is positive then the geometric progression will be of same sign as the first term of the sequence that is, positive.
-
If the common ratio ‘r’ is negative then the geometric progression will be of same sign as the first term of the sequence that is, negative.
-
If the common ratio ‘r’ is greater than 1, then the geometric progression will be in the exponential growth towards positive infinity.
-
If the common ratio ‘r’ is less than -1, then the geometric progression will be in the exponential growth towards (unsigned) infinity, due to the alternating sign.
-
If the common ratio ‘r’ is between -1 and 1(not zero), then the geometric progression will be exponential decay toward zero.
-
If the common ratio ‘r’ is zero, then the result will remain zero.
What is a Geometric Series?
When we add the terms of the geometric progression then that sum is the geometric series. Like, the GP, the ratio between every consecutive term is always constant.
The geometric series is in the form of
a+ ar+ ar2+ ar3+ …+ arn
where a is the first term of the series and r is the common ratio.
Formula of nth term or the general term of Geometric Series
If a is the first term, r is the common ratio and n is the total number of the terms, then the formula for nth term is given by
an = a.rn-1
Example
What is the 6th term of the series 2 + 4 + 8 + 16 +…?
Solution:
In the given series a = 2 and r = 2
So we will put the values in the formula of nth term of the series.
Here n = 6 as we have to find the 6th term.
a6 = 2.26-1
= 2 .32
= 64
So the 6th term of the series will be 32.
Sum of a Finite Geometric Series
If r ≠ 1
If a is the first term and r is the common ratio of the series with n number of terms, then the sum of the series
a+ ar+ ar2+ ar3+ …+ arn
will be
Example
Find the sum of the given geometric progression
Solution:
Given
a = 2 (first term)
r = 2 (common difference)
n = 5 (as the total number of terms of the series is 5)
Now we will put the values in the formula
If r = 1
If r =1 then the series will be in the form of
a + a + a + a +…..a (nth term)
The sum of the n terms will be
Sn = an
Sum of an Infinite Geometric Series
If we have to find the sum of the infinite geometric series then we will use the different formula.
When -1 < r <1 and n is infinite that is, ∞, then rn will tend to zero
So in the above formula of the sum of finite geometric series , rn is 0 and it will become a new formula that is,
Example
Find the sum of the series.

Solution:
a = 1 and r = 1/3
As we can see that -1 < r < 1, then we can use the formula

Geometric Mean
Geometric Mean is the average of two numbers. If a and b are the two numbers then the geometric mean will be
GM = √ab
Example
Find the geometric mean of 2 and 18.
We can use the above formula to calculate the geometric mean.
a = 2 and b = 18

Here we can see that the sequence 2, 6, 18 is a geometric progression.
Geometric Mean of more than two numbers
We can calculate the geometric mean of more than two numbers also as for calculating the geometric mean we have to multiply all the numbers and then take the nth root of that number. that is, If we are multiplying two numbers, we are taking the square root, as we had taken in the above example.
If we will multiply three numbers then we will take the cube root. Likewise, if we are multiplying n number of terms then we will take the nth root of the number.
GM = n√ (a1 × a2 × ... × an)
Example
What is the Geometric Mean of 1, 3, 9, 27 and 81?
Solution:
Given
a1 = 1
a2 = 3
a3 =9
a4 = 27
a5 = 81
First we will multiply the given numbers
1 × 3 × 9 × 27 × 81 = 59049
Then take the 5th root ( that is, the nth root where n = 5)
5√59049 = 9
Geometric Mean = 5√ (1 × 3 × 9 × 27 × 81) = 9
We can insert two or more numbers between the two given numbers to form a Geometric progression.
Let G 1, G2 ,…, G n be n numbers between positive numbers a and b such that
a, G 1, G 2, G 3,…, G n, b is a G.P.
Here, b is the (n + 2) th term, that is,

Thus, n numbers between a and b is as follows:

Example
Insert 2 numbers between 1 and 64 such that the resulting sequence is a G.P.
Solution:
Let G 1 and G2 ,be the two numbers between 1 and 64 such that
1, G 1, G2 , 64
the sequence is in G.P.
Here, a4 = 64
Hence r3 = 64 (the cube root of 64)
Thus, G 1 = ar = 1.4 = 4
G2 = ar2 = 1.42 = 16
Hence, two numbers between 1 and 64 are 4 and 16 which in turn are making a Geometric sequence.
1, 4, 16, 64
More Readings
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Click Here Know MoreAsk a Doubt
Get your questions answered by the expert for free