Oxidation and Reduction
Table of Content |
Classical Concept of Oxidation
 The term oxidation was first used to describe chemical reactions in which oxygen was added to an element of a compound. The phenomenon of combustion was the earliest example of oxidation. Later on the term oxidation was extended to describe many more reactions which occurred without the use of even oxygen. Lets try to find out what is answer of the question, What is oxidation ! according to classical concept.
The term oxidation was first used to describe chemical reactions in which oxygen was added to an element of a compound. The phenomenon of combustion was the earliest example of oxidation. Later on the term oxidation was extended to describe many more reactions which occurred without the use of even oxygen. Lets try to find out what is answer of the question, What is oxidation ! according to classical concept.
-
Addition of Oxygen: Reduction is a chemical reaction in which oxygen is removed from any chemical species (atom, ion or molecule).
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
S + O2 → SO2
2CO + O2 → 2CO2
Na2SO3 + H2O2 → Na2SO4 + H2O -
Removal of Hydrogen : Oxidation is a chemical reaction in which hydrogen is removed from any chemical species (atom, ion or molecule).
H2S + Cl2 → 2HCl + S
4HI + O2 → 2H2O + 2I2
4HI + MnO2 → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2 -
Addition of an Electronegative Element: Oxidation is a chemical reaction in which an electronegative element is added into any chemical species (atom, ion or molecule).
Fe+ S → FeS (Oxidation of iron)
SnCl2 + Cl2 → SnCl4 (Oxidation of stannous chloride)
 2Fe + 3F2 → 2FeF3 (Oxidation of iron)
2Fe + 3F2 → 2FeF3 (Oxidation of iron)
-
Removal of an Electropositive Element: Oxidation is a chemical reaction in which an electropositive element is removed from any chemical species (atom, ion or molecule).
2KI + H2O2 → 2KOH + I2 (Oxidation of potassium iodide)
2K2MnO4 + Cl2 → 2KCl + 2KMnO4 (Oxidation of potassium manganate)
2KI + Cl2 → 2KCl + I2 (Oxidation of potassium iodide) - A substance which brings oxidation is known as oxidizing agent.
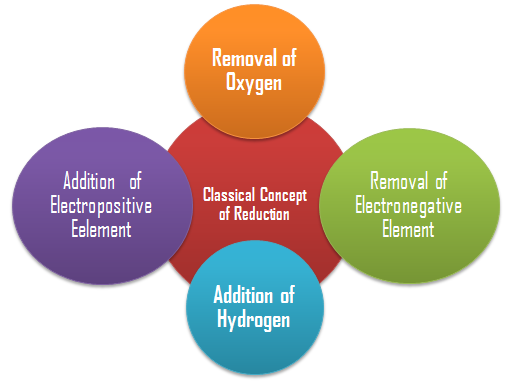
Classical Concept of Reduction
-
Removal of Oxygen: Reduction is a chemical reaction in which oxygen is removed from into any chemical species (atom, ion or molecule).
CuO + C → Cu + CO
H2O + C → CO + H2
2CO + O2 → 2CO2
Fe3O4 + 4H2 → 3F2 + 4H2O -
Addition of Hydrogen : Reduction is a chemical reaction in which hydrogen is added to any chemical species (atom, ion or molecule).
Cl2 + H2 → 2HCl
S + H2 → H2S
C2H4 + H2 → C2H6 -
Removal of an Electronegative Element: Reduction is a chemical reaction in which an electronegative element is removed from any chemical species (atom, ion or molecule). 2HgCl2 + SnCl2 → Hg2Cl2 + SnCl4 (Reduction of mercuric chlorine)
2FeCl3 + H2 → 2FeCl2 + 2HCl (Reduction of ferric chloride)
2FeCl3 + H2S → 2FeCl2 + 2HCl + S (Reduction of ferric chloride)
-
Addition of an Electropositive Element: Reduction is a chemical reaction in which an electropositive element is added any chemical species (atom, ion or molecule).
HgCl2 + Hg → Hg2Cl2 (Reduction of mercuric chloride)
CuCl2 + Cu → Cu2Cl2 (Reduction of cupric chloride) -
The substance which brings reduction is known as reducing agent.
-
A substance, which undergoes oxidation, acts as a reducing agent while a substance, which undergoes reduction, acts as an oxidizing agent.
Mg, S, Cu, Na2SO3, H2S, HI, H2, C, KI are reducing agents, while O2, Cl2, F2, H2O2, MnO2, FeCl3, CuCl2, Fe3O4, CuO, etc., are oxidizing agents in the above examples.
-
All oxidation and reduction reactions are complimentary of one another and occur simultaneously, one can not take place without the other.
-
No single oxidation and no single reduction process is known. The simultaneously oxidation and reduction reactions are generally termed as redox reactions. e.g., 2FeCl3 + SnCl2 → 2FeCl2 + SnCl4 or 2Fe3+ + Sn2+ → 2Fe2+ + Sn4+
In above example iron undergoes reduction from +3 to +2 and tin undergoes oxidation from +2 to +4.
Modern Concept of Oxidation & Reduction
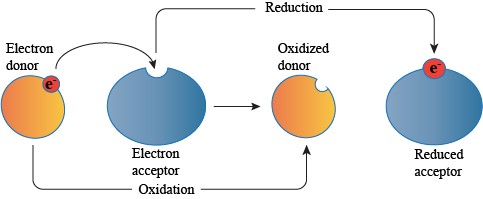
According to the modern concept, loss of electrons is oxidation whereas gain of electrons is reduction.
-
Examples of oxidation reactions are:
Na → Na+ + e
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e
Sn2+ → Sn4+ + 2e
H2O2 → O2 + 2H+ + 2e
2S2O32– → S4O62– + 2e
[Fe(CN)6]4– → [Fe(CN)6]3– + e
MnO42– → MnO4– + e -
Examples of reduction reactions are:-
Cl2 + 2e → 2Cl
S + 2e → S2–
Cu2+ + 2e → Cu
MnO4– + 8H+ + 5e → Mn2+ + 4H2O
Cr2O72– + 14H+ + 6e → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
H2O2 + 2H+ + 2e → 2H2O - Oxidation and reduction can be represented in a general way as shown below:

M4- → M3- → M2- → M- → M0 → M+ → M2+ → M3+ → M4+

- In a redox process the valency of the involved species changes. The valency of a reducing agent increases while the valency of an oxidizing agent decreases in a redox reaction. The valency of a free element is taken as zero.
-
Decrease in valency When there is no change in valency it means there is no oxidation or reduction, e.g.,
BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl or BaSO4 → Ba2+ + SO42– (No change in valency)
Watch this Video for more reference
Conclusion
-
Oxidation is a process in which one or more electrons are lost or valency of the element increases.
-
Reduction is a process in which one or more electrons are gained or valency of the element decreases.
-
Oxidizing agent is a material which can gain one or more electrons, i.e., valency decreases.
-
Reducing agent is a material which can lose one or more electrons, i.e., valency increases.
-
Redox reaction involves two half reactions, one involving loss of electron or electrons (oxidation) and the other involving gain of electrons or electrons (reduction).
|
Summary |

Question 1: Which of the following chemical reactions represent oxidation process?
a. Cl2 + 2e → 2Cl
b. S + 2e → S2–
c. 2S2O32– → S4O62– + 2e
d. MnO4– + 8H+ + 5e → Mn2+ + 4H2O
Question 2: According to the modern concept, oxidation is the process of
a. gain of electrons
b. lose of electrons
c. addition of hydrogen
d. removal of hydrogen
Question 3: Which of the following conditions does not represent oxidation?
a. Removal of hydrogen.
b. Addition of oxygen.
c. Removal of electropositive element.
d. Addition of electrons.
Question 4: Which of the following statements is incorrect ?
a. Oxidation is a process in which one or more electrons are lost or valency of the element increases.
b. Reduction is a process in which one or more electrons are gained or valency of the element decreases.
c. Oxidizing agent is a material which can gain one or more electrons,
d. Reducing agent is a material whose valency decreases during reaction.

|
Q.1 |
Q.2 |
Q.3 |
Q.4 |
|
c |
b |
d |
d |
Related Resources
-
Click here to know the syllabus of chemistry for IIT JEE
-
Have a look at past year papers of IIT JEE
-
You can refer to redox reactions.
To read more, Buy study materials of Redox Reactions comprising study notes, revision notes, video lectures, previous year solved questions etc. Also browse for more study materials on Chemistry here.
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More