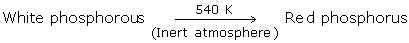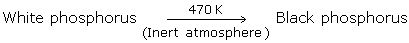Phosphorus Allotropic Forms
Table of Content |
Allotropes and Allotropy
The occurrence of an element in more than one physical shape is called Allotropy. The diverse physical types of a similar element are called Allotropes.
Allotropes have diverse physical properties, however, comparable chemical properties.
Phosphorus exists in a few allotropic structures. Of these, the three principle structures are white phosphorus, black phosphorus, and red phosphorus. However, another form of phosphorus that is violet phosphorus also exists.
Fig. 1: Allotropes of Phosphorus with Physical Properties
Fig. 2: The Interconvertible forms of all Allotropes of Phosphorus
White Phosphorus
-
It is a delicate, waxy and translucent solid.
-
It is undissolvable in water, yet solvent in carbon disulfide or carbon tetrachloride.
-
It breaks down in boiling caustic soda in a latent air to give sodium hypophosphite and phosphine.
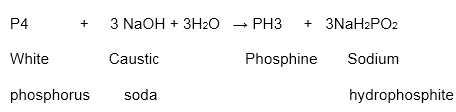
Structure
Fig. 3: Structure of White Phosphorus
Fig. 4: Bond Length of White Phosphorus
-
It is exceptionally harmful and to a great degree reactive.
-
It is found as tetrahedral P 4 particles.
-
Every phosphorus particle is covalently attached to three different atoms of phosphorus.
-
These particles are bonded to each other by weak Van der Waal's forces of attraction. It has a low melting point of 44°C.
-
The bond angle in a P 4 particle is 60°, which is significantly less than the normal or hypothetical bond angle.
-
This precise strain in the particle makes white phosphorus highly unstable and, therefore, exceptionally reactive.
-
White phosphorus ignites suddenly in air at around 35°C, that is, at a temperature marginally higher than room temperature, to frame phosphorus pentoxide. Thus, it is kept in water.
P4 + 5O2 → 2P2O5 or P4O10
Phosphorus pentoxide
-
In contact with moist air, white phosphorus gets oxidized. This reaction is connected with the discharge of light. As an outcome, it sparkles oblivious.
-
White phosphorus displays chemiluminescence.
Red Phosphorus
-
Upon heating white phosphorus to around 250 degrees Celsius within the sight of daylight, red phosphorus is obtained.
-
Red phosphorus is an iron-gray radiant crystalline solid.
-
It is non-poisonous, odorless and insoluble in water and also in carbon tetrachloride. It doesn't break up in boiling caustic soda, however, disintegrates in alcoholic potash.
-
It exists as a polymeric solid.
Fig. 5: A molecule of Red Phosphorus
-
It is steady under ordinary conditions and doesn't ignite in air.
-
It experiences burning just when warmed to around 400°C.
-
Red phosphorus doesn't show chemiluminescence.
Black Phosphorus
Black Phosphorus can be prepared from white phosphorus as follows:
-
Of all the three allotropes, black phosphorus is the most stable.
-
It has a layered structure and is a highly polymerized form of phosphorus.
Fig. 6: The Layered Structure of Black Phosphorus
-
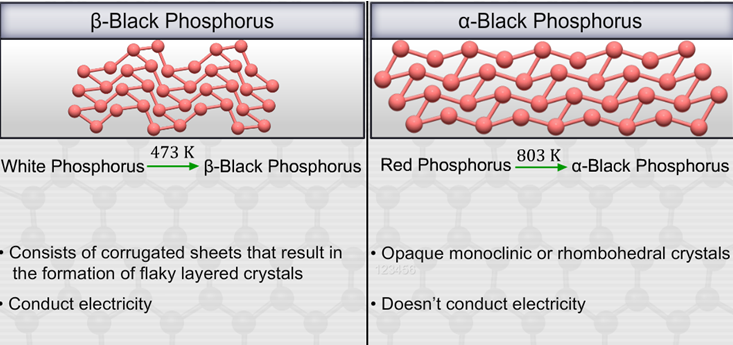
It is found in two forms, namely, alpha black phosphorus and beta black phosphorus.
Fig. 7: Preparation and Properties of Alpha Black Phosphorus and Beta Black Phosphorus
A few physical properties of three forms of Phosphorus are given below:
Uses of Phosphorus
Phosphorus compounds assume a vital part in life forms. P is a basic constituent of animal and plant matter. It is available in bones, brain and blood of animal body and furthermore in living cells. A few of its compounds find applications in industries. The most essential of these chemicals are orthophosphoric acid and phosphatic composts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the meaning of allotropes?
Sol. The occurrence of an element in more than one physical shape is called allotropy. The diverse physical types of a similar element are called allotropes.
Allotropes have diverse physical properties, however, comparable chemical properties.
Q2. What is an example of allotrope?
Sol. Phosphorus exists in a few allotropic structures. Of these, the three principle structures are white phosphorus, black phosphorus, and red phosphorus. However, another form of phosphorus that is violet phosphorus also exists.
Q3. What is yellow phosphorus?
Sol. Yellow phosphorus is another name for white phosphorus, an allotrope of phosphorus.
Q4. Why is white phosphorus stored in water?
Sol. White phosphorus ignites suddenly in air at around 35°C, that is, at a temperature marginally higher than room temperature, to frame phosphorus pentoxide. Thus it is kept in water.
P4 + 5O2 → 2P2O5 or P4O10
Phosphorus pentoxide
Watch this Video for more reference
More Readings
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Click Here Know MoreAsk a Doubt
Get your questions answered by the expert for free