Sulphur Dioxide
Table of Content |
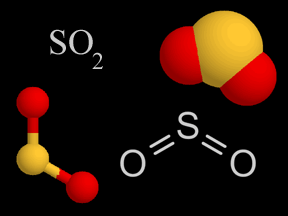
In the colored particle models, sulphur is yellow and oxygen is red.
Fig. 1: Four diverse ways scientists use to demonstrate a particle of sulfur dioxide
Methods to Prepare Sulphur Dioxide Gas
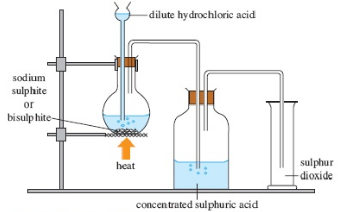
Sulphur dioxide is set up in the laboratory by the activity of dilute sulphuric acid on sulphites
Na2SO3 + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O + SO2↑
Sodium sulphite Sulphuric acid Sodium sulphate water Sulphur dioxide
Fig. 2: Laboratory preparation of sulphur dioxide
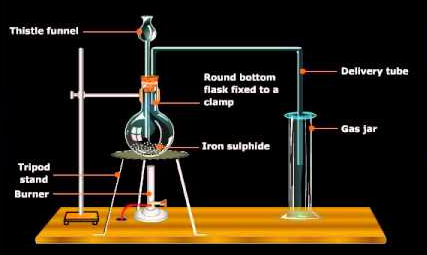
Commercially, vast volumes of sulphur dioxide are set up by cooking a sulphide ore, for example, iron sulfide. The gas is liquefied subsequent to drying under 25 atm pressure and stored in steel barrels.
Roasting,
Fe2S3 + 4O2 → FeO + 3SO2
Liquefaction 25 atm
So2 (g) → SO2(l)
Fig. 3: Industrial preparation of sulphur
Sulphur dioxide is likewise obtained on an extensive scale by blazing sulphur in air.
Physical Properties of Sulphur Dioxide
-
Sulphur dioxide is a dull gas with a pungent smell similar to smoldering sulphur.
-
It is one of the most straightforward gasses to melt, since it consolidates at room temperature under a pressure of 2 atm.
Chemical Properties of Sulphur Dioxide
-
It is an acidic oxide that is readily dissolvable in water.
-
It breaks up in water to give sulphurous acid.
SO2 + H2O → H2SO3
Sulphur dioxide Water Sulphurous acid
-
It reacts promptly with sodium hydroxide solution and structures sodium sulphite.
SO2 + 2NaOH → Na2SO3 + H2O
Sulphur dioxide Sodium hydroxide Sodium sulphate Water
-
In the event that more sulfur dioxide is passed into this arrangement, sodium hydrogen sulphite is framed.
SO2 + Na2SO3 → H2O + 2NaHSO3
Sulphur dioxide Sodium sulphate Water Sodium hydrogen sulphate
(excess)
-
The sulphur particle in a sulphur dioxide atom is tetravalent. Subsequently, it can augment it's covalency to six by specifically consolidating with elements like O2 and Cl2 to shape the comparing addition compounds.
Example: It reacts with chlorine within the presence of charcoal as an impetus to give sulphuryl chloride (SO2Cl2).
Charcoal
SO2 + Cl2 → SO2Cl2
Sulphur dioxide Chlorine (Catalyst) Sulphuryl Chloride
- Within the sight of vanadium pentoxide as an impetus, it gives sulphur trioxide.
V2O5
2SO2 + O2 → SO3
Sulphur dioxide Oxygen Sulphur trioxide
- Within the sight of moisture, it can start giving nascent oxygen, and, along these lines, go about as a reducing agent.
Example: It reduces ferric salts to ferrous salts, and halogens to halogen acids.
2Fe3+ + SO2 + 2H2O → 2Fe2+ + SO42- + 4H+
Ferric Sulphur water Ferrous
salt dioxide salt
X2 + SO2 + 2H2O → SO42- + 2X - + 4H+
Halogen Sulphur water halogen
dioxide acid
Identifying Tests for Sulphur Dioxide Gas
- It decolorizes acidified KMnO4 solution
5SO2 + 2KMnO4 + 2H2O → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 2H2SO4
Sulphur potassium potassium Manganese Sulphuric
dioxide permanganate sulphate sulphate acid
- It turns a filter paper moistened with acidified K2Cr2O7 solution green
3SO2 + K2Cr2O7 + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2Cr2(SO4)3 + H2O
Sulphur Potassium Sulphuric potassium chromium
dioxide dichromate acid sulphate sulphate
- It turns starch iodate paper blue
5SO2 + 2KIO3 + 4H2O → 2KHSO4 + 3H2SO4 + I2
Sulphur potassium Water potassium Sulphuric Iodine
dioxide iodate hydrogen acid
sulphate
Structure of Sulphur Dioxide
It is angular shaped with an O-S-O bond edge of 119.50. Take note of that despite the fact that sulphur dioxide has two unique sorts of pi bonds, i.e. p pi - p pi and d pi - p pi.
The two sulphur-oxygen bond lengths are equivalent. This shows sulphur dioxide is a resonance hybrid of two canonical structures.
Fig. 4: Resonance forms of sulphur dioxide
Fig. 5: Bond angle of sulphur dioxide
Uses:
The different uses of sulphur dioxide are:
1) In the assembling of sulphites, sulphuric acid, and hydrogen sulphite.
2) In the sugar business, for refining and decolorizing sugar.
3) For refining lamp oil, and other petroleum items.
4) As a disinfectant.
5) As a fumigant.
6) For dying fragile articles.
7) As antichlor, to expel the overabundance chlorine from substances those have been faded by chlorine.
8) As a glue solvent.
9) As a refrigerant in refrigerators.
10) As an additive for wines, meat, dry natural products and so on.
Fig. 6: Summary of the uses of sulphur
Watch this Video for more reference
More Readings
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More