Linear Inequalities
Table of content |
|
|
Inequality
Inequality is basically a relation which shows that the two given things are not equal in any sense like in weight, height, color etc.
In mathematics, if two values are not equal then also there is a relation between them and that relation is called Inequality.
Inequality symbol
For the things which are equal we use a “=” sign but for the things which are not equal to each other, we use different signs.
There are some common symbols which are used for inequality:
|
1. |
< |
is less than |
|
2. |
> |
Is greater than |
|
3. |
≤ |
Is less than or equal to |
|
4. |
≥ |
Is greater than or equal to |
|
5. |
≠ |
Is not equal to |
Example
What is the relation between 5 and 7?
Solution: Here we will use the symbol of inequality to represent the relation between 5 and 7.
Or
7>5 (7 is greater than 5)
This is one and the same thing. This shows that if we flip the values, we have to flip the symbols also.
What is an Inequality Notation?
Inequality notation is the way to represent the inequality of a statement of numbers:
- Inequality Notation: This is the way to write the statement using the inequality symbol. Like:
x>5 (x is greater than 5)
- Set Notation: This is the way to write the statement as a set of points. Like:
{x: x R, x>5}, reads as ‘x is a real number and x is greater than 5’.
- Interval Notation: This is the way to write the relation of values as an interval or a part of the number line. Like:
(5, ∞) reads as ‘the interval from 5 to ∞’.
Here the bracket [ ] means including the particular number and bracket ( ) means excluding. If we write the above solution as [5, ∞), then it reads as ‘interval from 5 to ∞ including 5’.
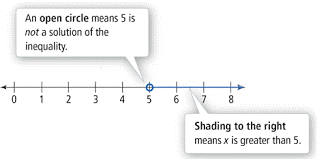
- Graph Notation: This is the illustrative way to represent the interval through the number line. Like:
(5, ∞), here 5 is not included in the interval so we will mark it with the open circle and then shade to the right to show that x > 5.
If we will draw a graph for [5, ∞), then we will mark it with closed circle and then shade it to right.
Linear Inequality
Linear Inequality is the inequality in an equation having linear function. It is same as linear equations just replacing the equality sign with the inequality symbols.
y = x + 1 (linear equation having equal sign)
y> x + 1 (linear inequality having greater than sign)
Linear Inequality with one variable
If there is only one variable in a linear function then it is linear inequality with one variable.
Example
25x < 400
There is only one variable “x” in the above linear function.
-
How can you solve an equation or inequality in one variable?
Both the linear equation and inequality has the same method to solve it.
Let’s understand it with the example:
Given: 25x < 400
We can solve it by putting values to x assuming x = 0, 1, 2 and so on.
x = 0, 0 < 400, this is true
x = 1, 25 < 400, this is true
x = 2, 50 < 400, this is true
x = 3, 75 < 400, this is true
x = 4, 100 < 400, this is true
Like this we can get the solution set of this inequality by putting values for x, but this is not possible for the bigger numbers. And it is time consuming also.so we can use the other two methods like:
-
Same number can be added or subtracted to the both sides of the linear inequality without changing the sign of inequality.
-
Same number can be multiplied or divided to both the sides.
Example
Solve 4x + 5 < 6x + 9
Solution: We can subtract 6x from both the sides.
4x – 6x < 6x + 4 – 6x
-2x < 4

As if we flip the sign the sign of inequality should also be flipped.
The solution set here is (-2, ∞) which says the set of all the real numbers greater than:
What is a Linear Inequality in two variables?
If there are two variables in a linear function then it is linear inequality with two variables.
Example
x + 3y < 9
There are two variables x and y in this linear inequality.to find the value of one variable we must know the value of other variable.
- How to solve a Linear Inequality with two variables?
We will solve the linear inequality, with the same method of solving linear equations.
We can assume the value of x as 0, 1, 2 and so on. So that we can find the solution set for the given problem.
Example
Solve x + 3y < 9 for the solution set.
Solution: We will find the pair of values of x and y for the solution set.
Let x = 0
0 + 3y < 9
3y < 9
This shows that if x = 0 then y could be less than 3 that is, 0, 1, 2. We will not include 3 here as it is less than three only not less than or equal to three. The solution set for this are:
Similarly we can find the solution set by assuming the value of x as 1, 2, 3 and so on.
How do you graph an Inequality?
Graph is the representation of the solution of the linear inequality on the Euclidean plane. First we have to draw the graph for the linear equation then we will shade the part having the solution set of linear inequality.
Graph of Linear Inequality in one variable
In the case of one variable the graph of linear inequality will be a number line only. As there is only on variable so only one line.
- Open circle: If there is an inequality with < and > sign, then we will use the open circle to represent it, which shows that, the particular number is not included in the solution.
Example
Draw a graph for x > -3
-
First draw a number line.
-
Then we will plot a point for x = -3 on the number line.
-
Mark it with an open circle as the -3 is not included in the solution.
-
As the inequality sign shows that x > -3, so we will shade the line to the right side.
-
Remember if there is less than sign then we will shade it to the left side.
- Close circle: If there is an inequality with ≤ and ≥ sign, then we will use the close circle to represent it, which shows that the particular number is included in the solution.
Example
Draw a graph for x ≥ 2
-
First draw a number line.
-
Then we will plot a point for x = 2 on the number line.
-
Mark it with a closed circle as the 2 is included in the solution.
-
As the inequality sign shows that x ≥ 2, so we will shade the line to the right side.
-
Remember if there is less than sign then we will shade it to the left side.
Graph of Linear Inequality in two variables
The solution of the linear inequality with two variables is represented by the half plane on the Euclidean plane.
Example
Draw graph for y>2x+1
Solution:
-
First of all we will solve the equation as the linear equation with equality sign to find the solution.
-
Then we will draw a line on the graph using the solution set that is, “y=”.
-
Here comes the step to find the solution of the inequality. if there is ≥ and ≤ sign then we will make a solid line which shows that the line is included in the solution or a dashed line for < and > sign which shows that the line is not included in the solution.
-
After plotting the line we will shade the lower region that is, below the line for < or ≤ sign or the upper region that is, above the line for > or ≥ sign.
-
That shaded part is the solution of the given linear inequality.
Graph of one Variable in coordinate plane
This is a special case as here we have vertical or horizontal line to represent the solution of the linear inequality.
Horizontal Line
y >-2
This shows that x could be anything but y will be -2 only. So we will make a dashed line for y = -2 first than shade the upper part as y > – 2.
Vertical Line
x> -3
This shows that y could be anything but x will be -3 only.So we will make a dashed line for x = – 3 first than shade the right part as x > – 3.
Word Problem
Billy and grey played cricket .grey scored 3 more runs than Billy, but together they scored less than 9 runs. What is the possible number of runs grey scored?
Solution:
Let the runs scored by Billy = B
Let the runs scored by grey = G
From the problem it is given that grey scored 3 more runs than Billy,
G = B + 3
They together scored less than 9
B + G < 9
We have to find G
So
B + G < 9
B + (B + 3) <9 (by putting value of G from 1st equation)
2B < 6
B < 3
Billy scored less than 3 runs, which means that Billy could have scored 0, 1 or 2 runs.
Grey scored 3 more runs than Billy did, so Grey could have scored 3, 4, or 5 goals.
More Readings