Revision Notes on Forests - Our Lifeline
What is a forest?
-
A forest is an area or a part of the land that is covered with trees and a wide variety of plants.
-
Not only this, forests form a complete ecosystem that includes various living organisms such as trees, shrubs, plants, microorganisms, wild animals and birds.
-
They also include non-living or abiotic factors such as sunlight, air, nutrients, water and rocks.
-
There are different kinds of forests present on the earth depending upon the geographical and climatic conditions of a particular region.
-
Forests serve various purposes for human beings as well as nature hence they are an important resource.

Figure 1: Different Forests in India
Forests are home of numerous of plant species
-
There are different kinds of trees found in the forest such as Neem, bamboo, Sheesham, fig, sal, amla and teak.
-
Along with trees, there are different herbs, shrubs, climbers, creepers, grasses and plants found in the forest.
-
These plants serve various purposes for the environment as well as human beings.
-
The forests grow by themselves.
-
There is no need to plant trees in the forest as the forests provide favourable environmental conditions to plants so that they can germinate and grow on their own.

Figure 2: Different Trees found in Forests
What is a crown?
The upper part or top of a tree is called its Crown.
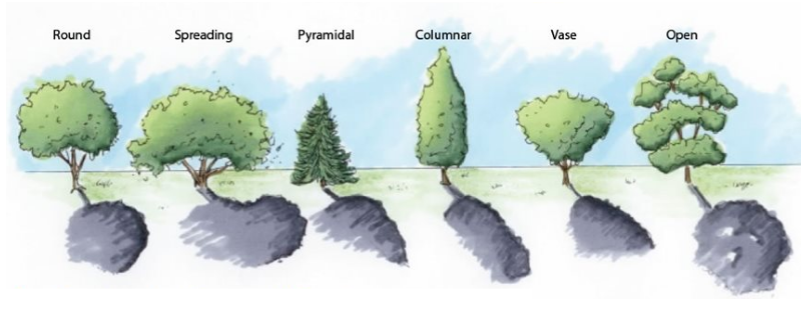
Figure 3: Different Crowns of Trees
What is canopy?
In the forest different trees grow tall together and their branches appear as the roof of the forest as no sky is visible through these trees. This is called Canopy.

Figure 4: Canopy
Stratification in Forests
Stratification is defined as dividing a natural habitat into several layers depending upon the heights of plants or vegetation of that area. This allows minimization of competition among the animals and allows them to survive easily. The number of layers a forest has depends upon the climate, temperature, availability of light, type of soils and rainfall. Generally, the trees of a forest are divided into following sections:
-
The Forest Floor: It comprises of the shed leaves, stems, bark and the top layer of soil.
-
The Herb Layer: It consists of plants without woody stem those grow above the ground such as grasses. They are usually less in number in the forests.
-
The Shrub Layer: It consists of plants small to medium sizes. This layer requires the most sunlight.
-
The Understory: It consists of plants that grow above the forest floor but lower than the canopy. They require less amount of light in order to grow.
-
The Canopy: It consists of the tree crowns. It is always exposed to sunlight.
-
The Emergent Layer: It consists of the topmost layer of trees. It is generally found in tropical forests.

Figure 5: Stratification in Forest
Forests are a habitat of many kinds of animals
-
Forests provide favourable environmental conditions, food and shelter to a variety of wild animals, insects and microorganisms.
-
The trees of the forest act as their shelter while a variety of plants and animals are their food.
-
Forests are a home to a variety of insects and microorganisms because the soil of the forest is highly fertile and therefore it provides favourable living conditions such as water and nutrients to these organisms.
-
Forests also support different food chains because of a complex biodiversity in the forests. Different organisms present on the earth are dependent on each other. For instance, herbivores feed on the plants and carnivores depend upon the herbivores. This chain of organisms being dependent on each other for their food is called a Food Chain.

Figure 5: Food Chain in Forest
What is humus?
It is a dark coloured substance found in the soil. Humus is made from dead and decaying organisms. The microorganisms live upon the decaying matter and convert it to humus.
Who are decomposers?
Animals that feed on dead and decaying plants and animals and convert them into humus are called decomposers.
How nutrients are recycled in the forest?
-
The nutrients present in the soil are used by plants, insects and microorganisms.
-
When they die, their remains are turned into organic matter by the decomposers.
-
This keeps the soil fertile in the forests and recycles the nutrients.

Figure 6: Recycling of Nutrients in Forests
Why forests are called green lungs?
-
We know that plants take up carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
-
Hence the plants in the forests provide oxygen to the animals and their animals provide carbon dioxide to the plants.
-
In this way, a balance of Oxygen and Carbon dioxide is maintained in the atmosphere in forests. This is a reason why forests are called Green Lungs.

Figure 7: Forests maintain the amounts of Carbon dioxide and Oxygen in the atmosphere
Do people live in the forest?
Yes, people from different tribes live in forests. These people are dependent upon the forest for food, water, shelter and medicines.
Why forests are called dynamic living entity?
-
All the organisms whether they are plants or animals depend on each other and help each other to survive in the forest.
-
The herbivores are dependent on the plants for their food.
-
The carnivores are dependent on the herbivores.
-
The decaying matter of dead animals, plants and their excreta enables the growth of more plants by providing them with adequate nutrients to grow.
-
The decomposers decay the dead matter in the forest and support the growth of plants. Hence forests are called Dynamic Living Entity.
How forests prevent floods and soil erosion?
-
Forests act as a natural absorber and allow the rainwater to seep into the earth. As a result, the water table of the area near the forest is high.
-
The Forests control the flow of water and prevent floods.
-
This is because the plants and trees prevent the rainwater from directly flowing away.
-
In this way, forests allow a regulated supply of water to the nearby streams.
-
Also, the roots of the plants bind the soil and prevent heavy rainfall always from flowing it away. Hence, they also prevent soil erosion.

Figure 8: Forests Prevent Floods

Figure 9: How Forests Prevent Soil Erosion
How forests prevent pollution?
-
Firstly, forests are a rich source of oxygen. Hence, the air in and around the forest is always fresh and clean.
-
Forests prevent strong winds or dust storm from flowing in the area.
-
The areas surrounding the forests generally have a cool climate and receive a good amount of rainfall.
-
The forests also absorb loud sounds of the vehicles on the highways nearby and hence prevent noise pollution in the areas around the forest.

Figure 10: How Forests Prevent Pollution
How forests preserve the water cycle?
-
We know that plants get rid of an excess of water through the process of transpiration.
-
In this process, the water is released as water vapour in the atmosphere.
-
Hence forests increase the water vapour content in the atmosphere.
-
This water vapour condenses and forms clouds which lead to increased rainfalls in the area.
-
This rainwater gets into the ground and increases the underground water levels.
-
Hence forests preserve the water cycle.

Figure 11: Forests Preserve the Water Cycle
| Significance of forests |
|
1. Forests are a natural habitat of a wide variety of animals and plants. |
|
2. They help in regulating the amount of Oxygen and Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. |
|
3. They prevent global warming by keeping the air clean as they take in all the carbon dioxide. |
|
4. They regulate the water cycle on the earth. |
|
5. They prevent air, water, land and noise pollutions in some or the other way. |
|
6. They are a rich source of different products that are used by human beings:
|

Figure 12: Forest Products
What is afforestation?
The process of planting trees in unproductive areas and thereby increasing the forest land on earth is called Deforestation. Afforestation helps in increasing the forest land and thus helps in improving the environment of the Earth. It also leads to several benefits that the forests provide us.
What is deforestation?
Demolishing the forest on a large scale is called Deforestation. Human beings undergo this process in order to find more space for extending their habitats. However, this leads to several ill effects such as:
-
Many animals and plants lose their natural habitat. Being unable to find a suitable environment to live, they may die or become extinct eventually. Hence deforestation results in loss of biodiversity.
-
It will lead to changes in the climate.
-
Without any trees, the water cycle gets disturbed and the soil dries out.
-
It will lead to increased air pollution as trees are the ones that can absorb greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and increase the oxygen content in the atmosphere.
-
It can lead to increased floods as the trees will no longer be there to regulate a steady flow of water.
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More
