Revision Notes on Circular& Rotational Motion
Circular Motion:-
- Uniform Circular Motion:-Circular motion is said to the uniform if the speed of the particle (along the circular path) remains constant.

-
Angular Displacement:-
Scalar form:- ?S = r?θ
Vector form:- 

-
Angular Velocity:-
-
Relation between linear velocity (v) and angular velocity (ω):-
Scalar form:- v = rω
Vector form:- 
-
Angular Acceleration:-

-
Relation between linear acceleration (a) and angular acceleration (α):-
 Scalar form:- a= rα
Scalar form:- a= rα
Vector form:- 
Here, tangential component, 
Radial component, 
- Relation betweenlinear acceleration (a), angular velocity (ω) and linear velocity (v):-
a=v2/r = ω2/r
- Equations of rotational kinematics:-
(a) Angular velocity after a time t second:- ω=ω0+αt
(b) Angular displacement after t second:- θ = ω0t + ½ αt2
(c) Angular velocity after a certain rotation:- ω2 – ω02 = 2αθ
(d) Angle traversed in ‘nth’ second:- θnth = ω0 +α/2 (2n-1)
- Time period:- It is the time taken by the particle to complete one rotation.
T= 2π/ω
- Frequency:- The number of rotations made by the particle per second is called the frequency of rotation.
If f is the frequency, the particle describes 2πf radians per second.
ω = 2πf
So, f = 1/T
-
Centripetal force:- The force, acting along the radius towards the center, which is essential to keep the body moving in a circle with uniform speed is called centripetal force. It acts always along the radius towards the center. A centripetal force does no work.
F = mv2/r = mrω2
- Centrifugal force:- Centrifugal force is the fictitious force which acts on a body, rotating with uniform velocity in a circle, along the radius away from the center. Magnitude of centrifugal force is,
F = mv2/r
-
Centripetal and centrifugal forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. They cannot be termed as action and reaction since action and reaction never act on same body.
-
Banking of Roads:-
Road offering no frictional resistance, θ = tan-1 (v2/rg)
Road offering frictional resistance, vmax = √rg(µ+tanθ/1-µtanθ)
- Bending of Cyclist:- θ = tan-1 (v2/rg)
(a) Velocity of the cyclist:- Greater the velocity, greater is his angle of inclination with the vertical.
(b) Radius of curvature:- Smaller the radius, greater is the angle with the vertical.
-
Time period of conical pendulum:-T = 2π √lcosθ/g
-
Motion in a vertical circle/looping the loop:-
The minimum velocity of the body, at the lowest point, required to take the body round a vertical circle is √5gr.
So, v = √5gr
The minimum tension in the string, at the lowest point, required to take the body around the vertical circle is equal to six times the weight of the body.
So, T1= 6 mg
(a) For lowest point A and highest point B, TA – TB = 6 mg
VA2 = VB2+4gl
VA≥√5gl
VB≥√gl
(b) Condition for oscillation:- VA?√2gl
(c) Condition for leaving circular path:- √2gl< VA?√5gl
- Non-uniform circular motion:-
(a) The velocity changes both in magnitude as well as in direction.
(b) The velocity vector is always tangential to the path.
(c) The acceleration vector is not perpendicular to the velocity vector.
(d) The acceleration vector has two components.
(i) Tangential acceleration at changes the magnitude of velocity vector and is defined as, at = dv/dt
(ii) Normal acceleration or centripetal acceleration ac changes the direction of the velocity vector and is defined as,ac = v2/r
(iii) The total acceleration is the vector sum of the tangential and centripetal acceleration.
So, a = √at2+ac2
Rotational Motion
-
Rigid Body:- A rigid body consists of a number of particles confined to a fixed geometrical shape and size in such a way that the distance between any pair of particles always remains constant.
-
Moment of Inertia (Rotational Inertia) I:- Moment of Inertiaof a body, about a given axis, is defined as the sum of the products of the masses of different particles constituting the body and the square of their distances from the axis of rotation. It depends upon two factors,
(i) Mass of body
(ii) Distribution of mass about the axis of rotation
(iii) Moment of inertia of a body should always be referred to as about a given axis, since it depends upon distribution of mass about that axis.
(iv) It does not depend upon the state of motion of rotating body. It is same whether the body is at rest, rotating slowly or rotating fast about the given axis.
I = ∑mr2
- Rotational Kinetic Energy:- Kr = ½Iω2 = ½ mr2ω2
So, I = 2Kr/ω2
- Radius Gyration:- Radius of gyration of a body about a given axis is that distance, at which if whole of the mass of the body were concentrated, it would have same moment of inertia as that of body.
I = MK2
So, K = √I/M
Again, Radius of gyration of a body about a given axis is defined as the square root of the mean of the squares of distances of various particles of the body from the axis of rotation.
So, K = √[r12+ r22+ r32+…./n]
- Center of mass for two particle system:-
? (a) xCM=(m1x1+ m2x2)/(m1+ m2)
(a) xCM=(m1x1+ m2x2)/(m1+ m2)
(b) vCM = (m1v1+ m2v2)/(m1+ m2)
(c) aCM = (m1a1+ m2a2)/(m1+ m2)
(d) vCM = dxCM/dt
(e) aCM = dvCM/dt = d2xCM/dt2
- System of mass for many particle system:-
xCM = ∑mixi / ∑mi
- Perpendicular axes theorem:- It states that the moment of inertia of a plane lamina, about an axis perpendicular to the plane lamina, is equal to the sum of the moments of inertia of the lamina about two mutually perpendicular axes lying in the plane of lamina and intersecting each other at the point where the perpendicular axis passes through the body.
I = Ix+Iy
- Parallel axes theorem:-

?It states that moment of inertia of a body, about an axis, is equal to the sum of the moment of inertia of the body about a parallel axis through its center of gravity and the product of the mass of body and the square of the distance between the two axes.
I = Ig+Mh2
Here, Ig is the moment of inertia of the body about an axis through its center of gravity G.
- Moments of Inertia of Various Objects:-

-
Moment of inertia of a particle having mass m:- I = mr2
-
Moment of inertia of a thin rod about an axis passing through its center and perpendicular to its length:-
? I =Ml2/12
-
Moment of inertia of a ring about an axis passing through its center and perpendicular to its plane:-
(a) About one of its diameters:- Id = ½ (MR2)
(b)About a tangent
(i) Tangent lying in the plane of ring:-I = 3/2 (MR2)
(ii) Tangent perpendicular to the plane of ring:-I = 2MR2
- Moment of inertia of a solid disc:-
(a) About an axis passing through its center and perpendicular to its plane:- I = ½ MR2
(b) About one of its diameters:- Id = ¼ (MR2)
(c) About a tangent:-
(i) Tangent lying in the plane of disc:-I = 5/4 (MR2)
(ii) Tangent perpendicular to the plane of disc:- I = 3/2 (MR2)
-
Moment of inertia of an annular disc:-
(a) About an axis passing through the center and perpendicular to the plane:-
(i) For a solid disc:- I = ½ MR2
(ii) For ring:- I = MR2
(b) About any of its diameter:-
(i) For a solid disc:- Id = ¼ (MR2)
(ii) For ring:- Id = ½ MR2
(c) About a tangent:-
(i) Tangent lying in the plane of disc:-
(1)For a solid disc:-I = 5/4 MR2
(2)For a ring:-I = 3/2 MR2
(ii) Tangent perpendicular to the plane of the disc:-
(1) For a solid disc:- I = 3/2 MR2
(2) For a Ring:- I = 2MR2
- Torque (
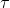 ) in vector form:-
) in vector form:-
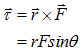
- Moment of inertia (I) and Torque (
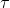 ?):-
?):-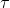 ? = Iα
? = Iα
Here α is the angular acceleration.
- Newton’s law in rotational motion:-
(a) First Law:- It states that everybody continues in its state of rest or of uniform rotational motion about a given axis unless it is completed by some external unbalanced torque to change that state.
(b) Second Law:- It states that the rate of change of angular momentum of a body is directly proportional to the impressed torque and takes place in the direction of torque. Mathematically, 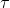 = Iα.
= Iα.
(c) Third Law:- It states that to every torque there is an equal and opposite torque.
-
Angular Momentum (L):-
?
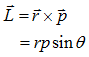
-
Moment of Inertia (I) and Angular momentum (L):-
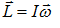
- Law of conservation of angular momentum:- The net angular momentum of an isolated system (no external torque), always remains constant.?
?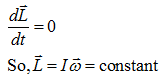
I1ω1=I2ω2
- Motion of a point mass attached to a string would over a cylinder capable of rotating about its axis of symmetry:-
Tension, T = mg/[1+(mR2/I)]
- Motion of a body rolling down an inclined plane without slipping:-
The maximum allowed angle for rolling without slipping.
(a) A cylinder rolling down the plane,
θmax = tan-1(3µ)
(b) A sphere rolling down the inclined plane,
θmax = tan-1[7/2 (µ)]
(c) A ring rolling down the inclined plane,
θmax = tan-1(2µ)
Here µ is the coefficient of sliding friction.
-
Angular impulse:-

-
Rotational work done:- W =τ?θ =τavθ
- Rotational power:-

You Might Like to Refer:
Neet coaching | IIT Coaching in Delhi | Best Coaching Institute for IIT
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Click Here Know MoreAsk a Doubt
Get your questions answered by the expert for free