Revision Notes on Kinematics
- Inertial frame of reference:- Reference frame in which Newtonian mechanics holds are called inertial reference frames or inertial frames. Reference frame in which Newtonian mechanics does not hold are called non-inertial reference frames or non-inertial frames.
- The average speed vav and average velocity
 of a body during a time interval ?t is defined as,
of a body during a time interval ?t is defined as,
vav= average speed
= ?s/?t
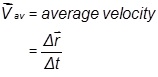
-
Instantaneous speed and velocity are defined at a particular instant and are given by
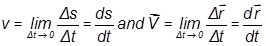
Note:
(a) A change in either speed or direction of motion results in a change in velocity
(b) A particle which completes one revolution, along a circular path, with uniform speed is said to possess zero velocity and non-zero speed.
(c) It is not possible for a particle to possess zero speed with a non-zero velocity.
- Average acceleration is defined as the change in velocity
 over a time interval ?t.
over a time interval ?t.
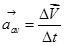
The instantaneous acceleration of a particle is the rate at which its velocity is changing at that instant.
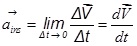
- The three equations of motion for an object with constant acceleration are given below.
(a) v= u+at
(b) s= ut+1/2 at2
(c) v2=u2+2as
Here u is the initial velocity, v is the final velocity, a is the acceleration , s is the displacement travelled by the body and t is the time.
Note: Take ‘+ve’ sign for a when the body accelerates and takes ‘–ve’ sign when the body decelerates.
- The displacement by the body in nth second is given by,
sn= u + a/2 (2n-1)
- Position-time (x vs t), velocity-time (v vs t) and acceleration-time (a vs t) graph for motion in one-dimension:
(i) Variation of displacement (x), velocity (v) and acceleration (a) with respect to time for different types of motion.
|
|
Displacement(x) |
Velocity(v) |
Acceleration (a) |
|
(a) At rest |
|
|
|
|
(b) Motion with constant velocity |
|
|
|
|
(c) Motion with constant acceleration |
|
|
|
|
(d) Motion with constant deceleration |
|
|
|
-
Scalar Quantities:- Scalar quantities are those quantities which require only magnitude for their complete specification.(e.g-mass, length, volume, density)
-
Vector Quantities:- Vector quantities are those quantities which require magnitude as well as direction for their complete specification. (e.g-displacement, velocity, acceleration, force)
-
Null Vector (Zero Vectors):- It is a vector having zero magnitude and an arbitrary direction.
When a null vector is added or subtracted from a given vector the resultant vector is same as the given vector.
Dot product of a null vector with any arbitrary is always zero. Cross product of a null vector with any other vector is also a null vector.
- Collinear vector:- Vectors having a common line of action are called collinear vector. There are two types.
Parallel vector (θ=0°):- Two vectors acting along same direction are called parallel vectors.
Anti parallel vector (θ=180°):-Two vectors which are directed in opposite directions are called anti-parallel vectors.
-
Co-planar vectors- Vectors situated in one plane, irrespective of their directions, are known as co-planar vectors.
-
Vector addition:-
Vector addition is commutative- 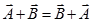
Vector addition is associative- 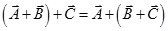
Vector addition is distributive- 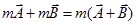
- Triangles Law of Vector addition:- If two vectors are represented by two sides of a triangle, taken in the same order, then their resultant in represented by the third side of the triangle taken in opposite order.
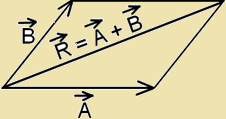
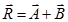
Magnitude of resultant vector 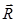 :-
:-
R=√(A2+B2+2ABcosθ)
Here θ is the angle between 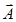 and
and 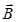 .
.
If β is the angle between 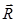 and
and 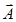 ,
,
then,
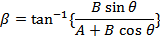
- If three vectors acting simultaneously on a particle can be represented by the three sides of a triangle taken in the same order, then the particle will remain in equilibrium.
So, 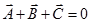
- Parallelogram law of vector addition:-
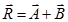
R=√(A2+B2+2ABcosθ),
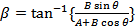
Cases 1:- When, θ=0°, then,
R= A+B (maximum), β=0°
Cases 2:- When, θ=180°, then,
R= A-B (minimum), β=0°
Cases 3:- When, θ=90°, then,
R=√(A2+B2), β = tan-1 (B/A)
- The process of subtracting one vector from another is equivalent to adding, vectorially, the negative of the vector to be subtracted.
So,
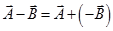
-
Resolution of vector in a plane:-
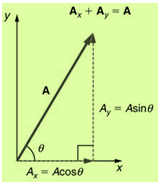
- Product of two vectors:-
(a) Dot product or scalar product:-
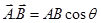 ,
,
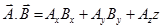
Here A is the magnitude of 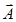 , B is the magnitude of
, B is the magnitude of 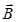 and θ is the angle between
and θ is the angle between 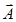 and
and 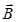 .
.
(i) Perpendicular vector:-
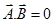
(ii) Collinear vector:-
When, Parallel vector (θ=0°),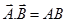
When, Anti parallel vector (θ=180°),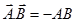
(b) Cross product or Vector product:-
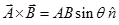
Or,
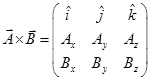
Here A is the magnitude of 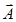 , B is the magnitude of
, B is the magnitude of 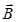 ,θ is the angle between
,θ is the angle between 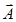 and
and 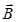 and
and 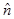 is the unit vector in a direction perpendicular to the plane containing
is the unit vector in a direction perpendicular to the plane containing 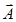 and
and 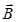 .
.
(i) Perpendicular vector (θ=90°):-
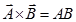
(ii) Collinear vector:-
When, Parallel vector (θ=0°), (null vector)
(null vector)
When, θ=180°, (null vector)
(null vector)
-
Unit Vector:- Unit vector of any vector is a vector having a unit magnitude, drawn in the direction of the given vector.
In three dimension,
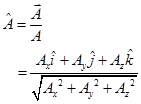
- Area:-
Area of triangle:- 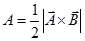
Area of parallelogram:- 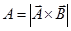
Volume of parallelepiped:- 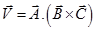
-
Equation of Motion in an Inclined Plane:
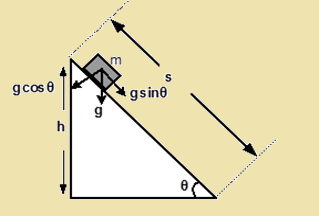 (i) Perpendicular vector :- At the top of the inclined plane (t = 0, u = 0 and a = g sinq ), the equation of motion will be,
(i) Perpendicular vector :- At the top of the inclined plane (t = 0, u = 0 and a = g sinq ), the equation of motion will be,
(a) v= (g sinθ)t
(b) s = ½ (g sinθ) t2
(c) v2 = 2(g sinθ)s
(ii) If time taken by the body to reach the bottom is t, then s = ½ (g sinθ) t2
t = √(2s/g sinθ)
But sinθ =h/s or s= h/sinθ
So, t =(1/sinθ) √(2h/g)
(iii) The velocity of the body at the bottom
v=g(sinθ)t
=√2gh
- The relative velocity of object A with respect to object B is given by
VAB=VA-VB
Here, VB is called reference object velocity.
- Variation of mass:- In accordance to Einstein’s mass-variation formula, the relativistic mass of body is defined as,
m= m0/√(1-v2/c2)
Here, m0 is the rest mass of the body, v is the speed of the body and c is the speed of light.
- Projectile motion in a plane:- If a particle having initial speed u is projected at an angle θ (angle of projection) with x-axis, then,
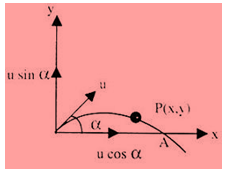
Time of Flight, T = (2u sinα)/g
Horizontal Range, R = u2sin2α/g
Maximum Height, H = u2sin2α/2g
Equation of trajectory, y = xtanα-(gx2/2u2cos2α)
- Motion of a ball:-
(a) When dropped:- Time period, t=√(2h/g) and speed, v=√(2gh
(b) When thrown up:- Time period, t=u/g and height, h = u2/2g
- Condition of equilibrium:-
(a) 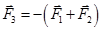
(b) |F1+F2|≥|F3|≥| F1-F2|
You Might Like to Refer:
CBSE class 7 maths| CBSE class 7 science | CBSE class 11 chemistry
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Click Here Know MoreAsk a Doubt
Get your questions answered by the expert for free











